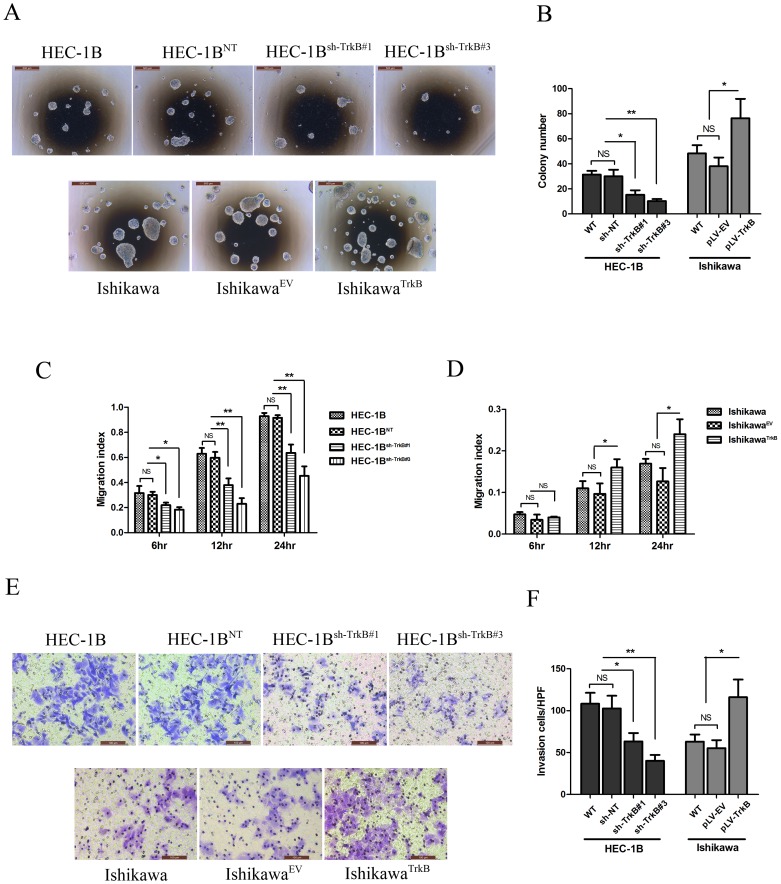
Figure 2. TrkB impacts tumor growth, migration, and invasion in vitro.
A. Anchorage-independent growth in soft agar of EC cell lines with silenced or overexpressed TrkB (40×). Representative images are shown. B. Mean +/− SD of the number of soft agar colonies for EC cell lines with silenced or overexpressed TrkB. HEC-1Bsh−TrkB#1 cells and HEC-1Bsh−TrkB#3 showed decreased colony formation ability compared with HEC-1BNT and wild type (*p<0.05, **p<0.01; NS, not significant), while IshikawaTrkB cells showed increased colony formation ability compared with IshikawaEV or parental Ishikawa cells (*p<0.05; NS, not significant). C. Cell migration was continuously tested by wound healing assay. HEC-1Bsh−TrkB#1 and HEC-1Bsh−TrkB#3 cells showed an obvious decrease in the migration index compared to HEC-1B or HEC-1BNT cells during the time period (*p<0.05, **p<0.01; NS, not significant). D. IshikawaTrkB cells exhibited an obvious increase in migration index compared to IshikawaEV or wild type (*p<0.05; NS, not significant). E. Cell invasion was measured in transwell chambers (200×). Representative images are shown. F. Cells were counted with a microscope in five random high-powered fields. Invasion ability was significantly decreased in HEC-1Bsh−TrkB#1 and HEC-1Bsh−TrkB#3 cells (*p<0.05, **p<0.01; NS, not significant), and it was enhanced in IshikawaTrkB cells (*p<0.05; NS, not significant). **p<0.01, *p<0.05 considered significant. Bars show mean ± SD. All experiments were carried out in triplicate and repeated at least three times.