Figure 6.
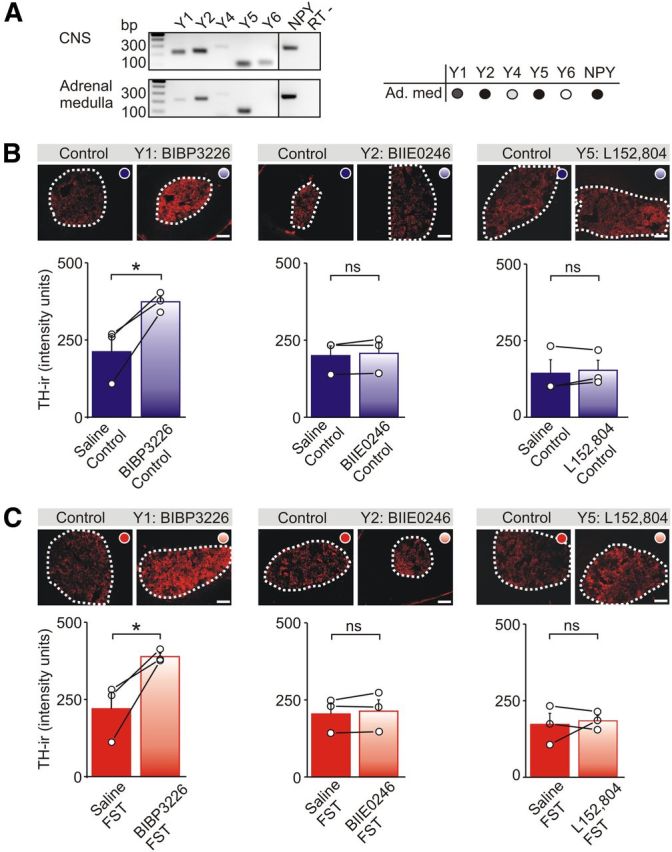
Y1 receptors tonically suppress TH expression in the adrenal medulla. A, RT-PCR of Y receptor expression in the adrenal medulla and CNS (positive control) of wild-type mice. Amplicons indicate the presence of mRNAs encoding Y1, Y2, Y4, and Y5 receptors and NPY in the adrenal medulla (Ad. med; results are tabulated on the right). The negative control (RT−) contained NPY primers but lacked reverse transcriptase. B, TH-IR in adrenal sections from saline-injected control mice or after injection with Y1, Y2, or Y5 antagonists. Group data shows that BIBP 3226 (a Y1 antagonist) significantly increased the basal level of TH-IR. Group data shows mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments (7–10 sections from each animal). C, TH-IR in adrenal sections from mice exposed to the FST and injected with either saline or Y1, Y2, or Y5 antagonists. Group data shows that only BIBP 3226 significantly increased the level of TH-IR. Group data shows mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments (7–10 sections from each animal). Scale bars, 100 μm. *p < 0.05.
