Figure 1.
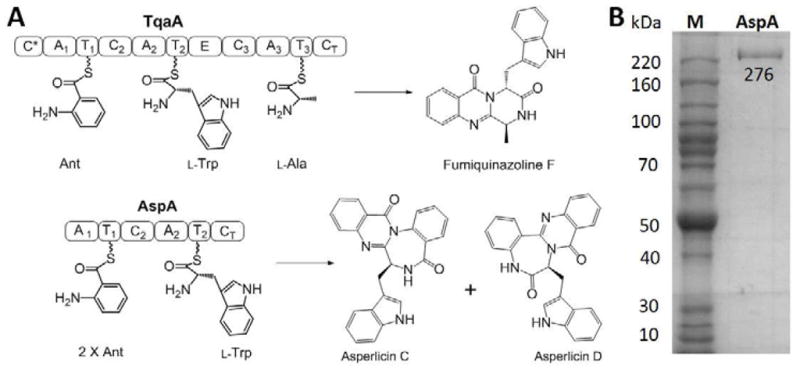
Heterologous expression of AspA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. (A) Amino acid building blocks for assembly of fumiquinazoline F (FQF), and asperlicins C and D. AspA is a 276 kDa two-module NRPS enzymes with the indicated Adenylation (A), Thiolation (T) and Condensation (C) domains. The terminal condensation domains (CT) of TqaA and AspA act as cyclization/release catalysts for Ant-D-Trp-L-Ala and Ant-Ant-L-Trp, respectively, presented as thioesters on the pantetheinyl arms of immediate upstream T domains. Intramolecular capture of the thioester carbonyl by the NH2 of Ant1 is the proposed common release mechanism. The subsequent transannular cyclizations and aromatizing dehydrations yield 6,6,6-tricyclic quinazolinedione (fumiquinazoline F) or tetracyclic 6,6,7,6 asperlicin C/D regioisomeric scaffolds, affected by the presence or absence of Ant2 in the tripepitidyl-S-thiolation domain intermediates. (B) SDS-PAGE gel of AspA expressed and purified from S. cerevisiae BJ5464-NgpA.
