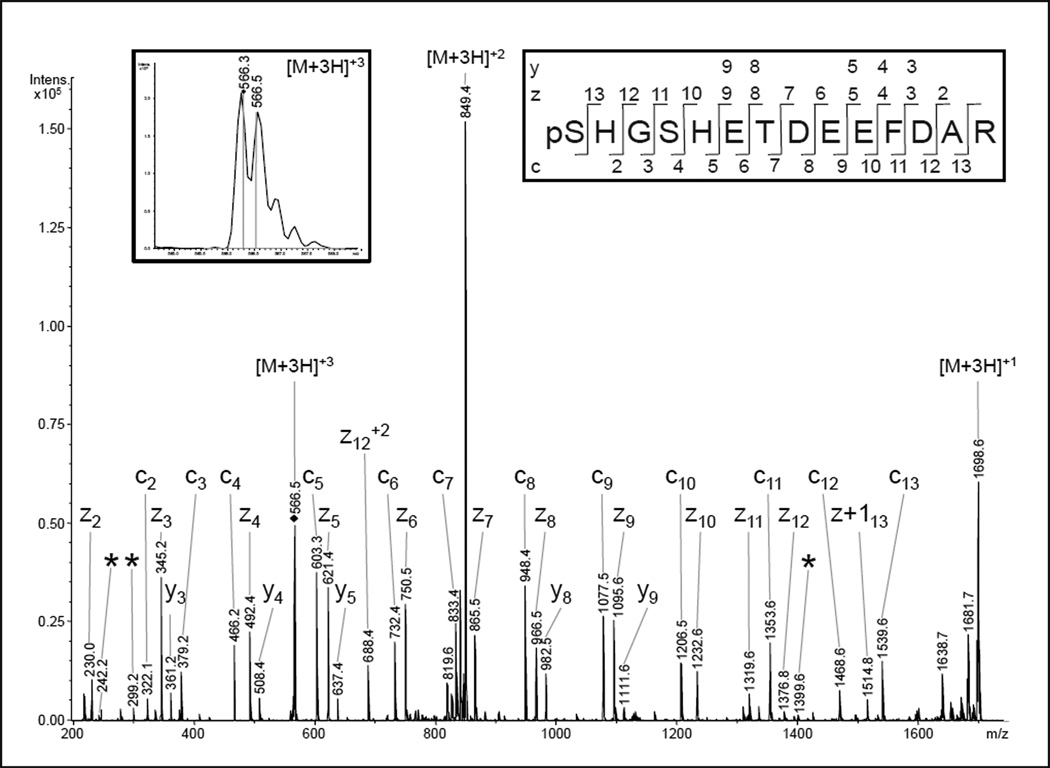
Fig 2.
NanoLC-ESI-MS/MS analysis of COX subunit Va. A phosphorylation at serine-4 was previously described for a peptide of the same sequence [27]. The presented ETD spectrum of the triply-charged ion (566.3 m/z) was matched to the peptide pSHGSHETDEEFDAR by the Mascot® search algorithm with scores of 94 for a phosphorylation at serine-1 and 72 in case of pSer4. The discrimination between these phosphorylation sites should be possible, as ions from the four N-terminal amino acids as well as the ions enabling the assignment of pSer1 were also present (c2, c3, z11, z12, z13). However, in comparison with the fragmentation behavior of the previously-identified pSer-4 peptide and the calculated fragment ion masses, three pSer4-specific fragments of low relative abundance were also present (*). Therefore, a HPLC co-elution and ion trap co-isolation of both phosphopeptides is likely and the spectrum presumably represents a mixed fragment ion pattern.