Figure 1. Central roles of HIF-1, mitochondria and signaling pathways in stem cell preconditioning.
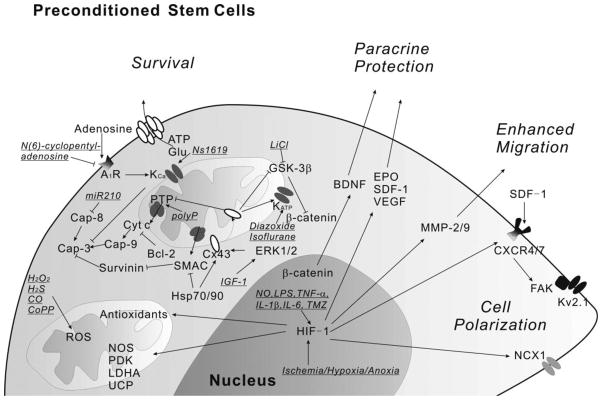
Ischemia, hypoxia, anoxia and some other insults increase HIF-1 expression. HIF-1 then regulates antioxidants, survival signals and many other genes related to cell adhesion, polarization, migration and paracrine protection. Mitochondria also play essential roles for improving cell viability responding to preconditioning insults. The underlined indicates the insults used.
Abbreviations: A1R, adenosine A1 receptor; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Cap, caspase; CoPP, cobalt protoporphyrin; Cx43, connexin-43; CXCR, CXC chemokine receptor; Cyt c, cytochrome c; EPO, erythropoietin; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; HIF-1, hypoxia-inducible factor-1; Hsp, heat shock protein; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; IL-1β, interleukin-1beta; IL-6, interleukin-6; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; miR, micro-RNA; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NCX-1, sodium-calcium exchanger-1; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; PDK, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; polyP, polyphosphate; PTP, permeability transition pore; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SDF-1, stromal-derived factor-1; SMAC, second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase; TMZ, Trimetazidine; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; UCP, uncoupling protein; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
