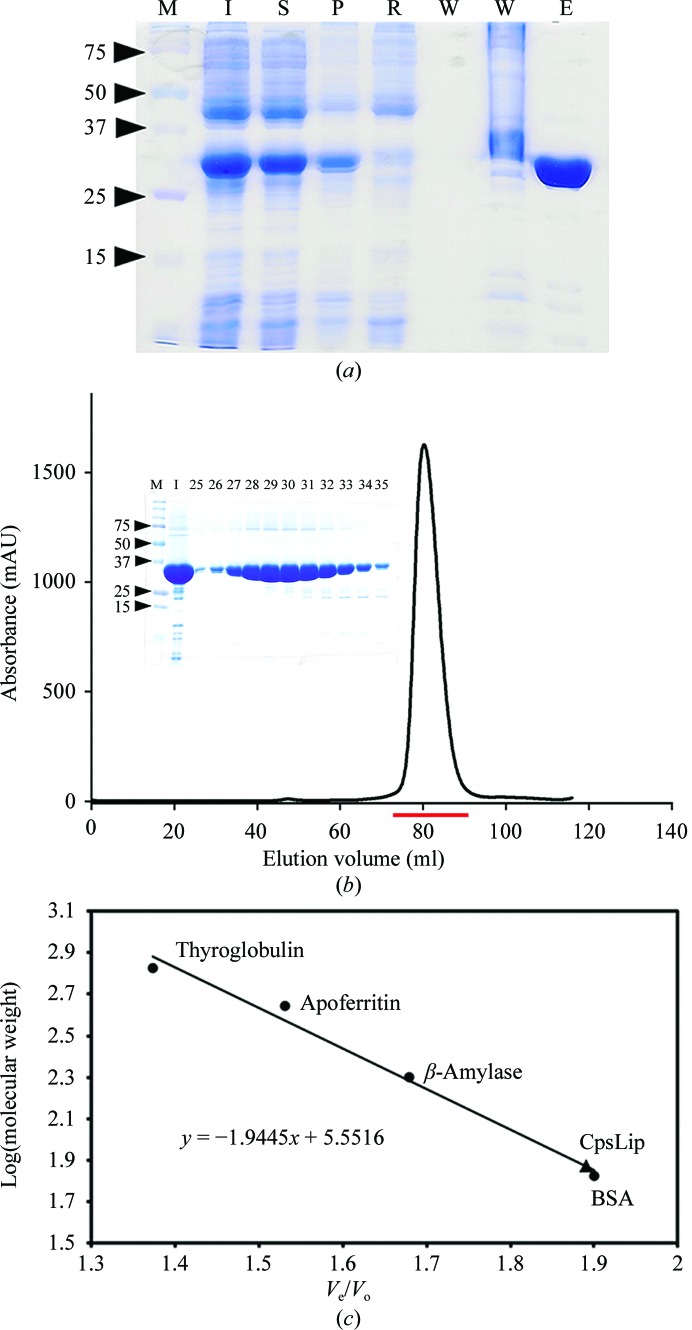
Figure 1.
Expression and purification of recombinant CpsLip. (a) 12% SDS–PAGE analysis of the expression and purification of CpsLip. Lane M, molecular-weight markers (labelled in kDa); lane I, induced fraction; lane S, soluble fraction; lane P, pellet; lane R, remaining fraction after flowing through the resin; lane W, washing fraction; lane E, elution fraction. (b) The size-exclusion chromatography profile of CpsLip from a Superdex 200 column. The injection sample (I) and several fractions, indicated by a red bar (fraction numbers from 25–35) in the chromatography profile, were visualized using a 12% SDS–PAGE gel (inset). (c) The column was calibrated at 298 K with globular protein standards that included thyroglobulin (669 kDa, V e = 58.4 ml), apoferritin (443 kDa, V e = 65.1 ml), β-amylase (200 kDa, V e = 71.4 ml) and BSA (67 kDa, V e = 80.8 ml). The void volume of the column (V o) was determined to be 42.5 ml using blue dextran (2000 kDa); V e is the peak elution volume. The V e/V o values were used to generate a standard curve; the molecular mass of CpsLip was determined from the standard curve. The elution volume indicated that CpsLip was a dimer in solution with an apparent molecular weight of 75 kDa (V e = 80.5 ml).