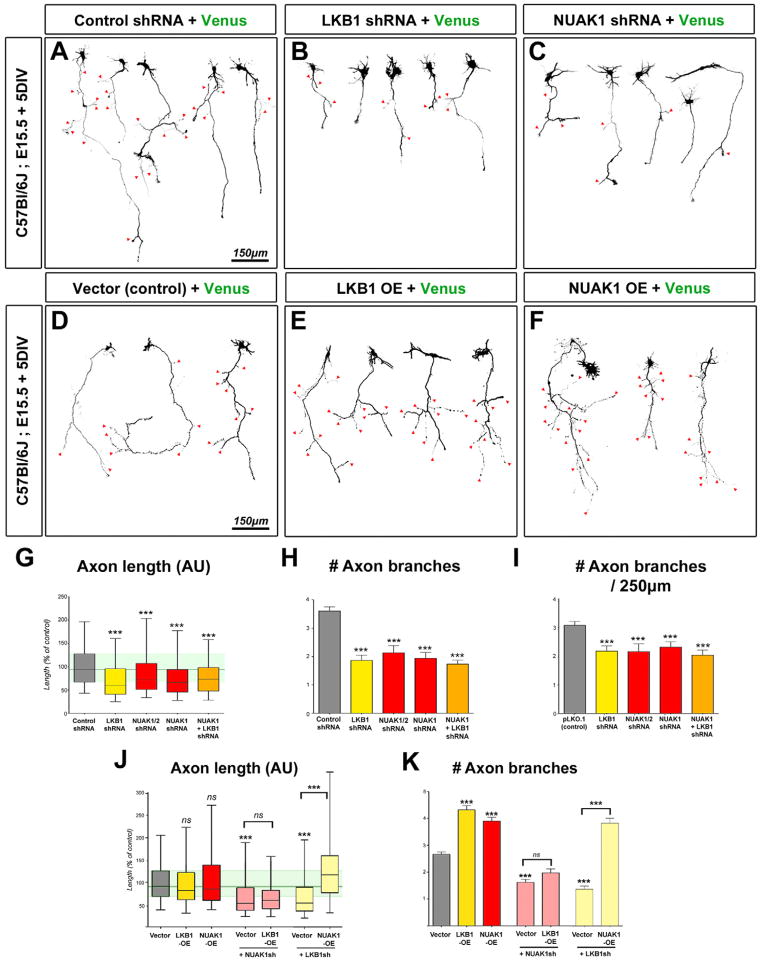
Figure 3. LKB1 regulates axon growth and branching in vitro through NUAK1.
(A–C) Representative neurons imaged after 5 day of culture in vitro (DIV) following inhibition of LKB1 (B) or NUAK1 (C) expression. (D–F) Overexpression of LKB1 (E) or NUAK1 (F) in 5 DIV cortical neurons induced the formation of supernumerary axonal branches. Red arrowheads in A–F point to axon branches. (G–I) Quantification of axon morphology shows that LKB1 or NUAK1 inhibition results in a shortened axon (G) and decreased collateral branch formation (HI). (J–K) Quantitation of axon length (J) or number of collateral branches at 5DIV (K) after overexpression of the indicated constructs. Data represent 25th, 50th and 75th percentile (G, J) or average value ±SEM (H–I, K). Statistical analysis: Mann-Whitney test. See also Fig. S3–S5.