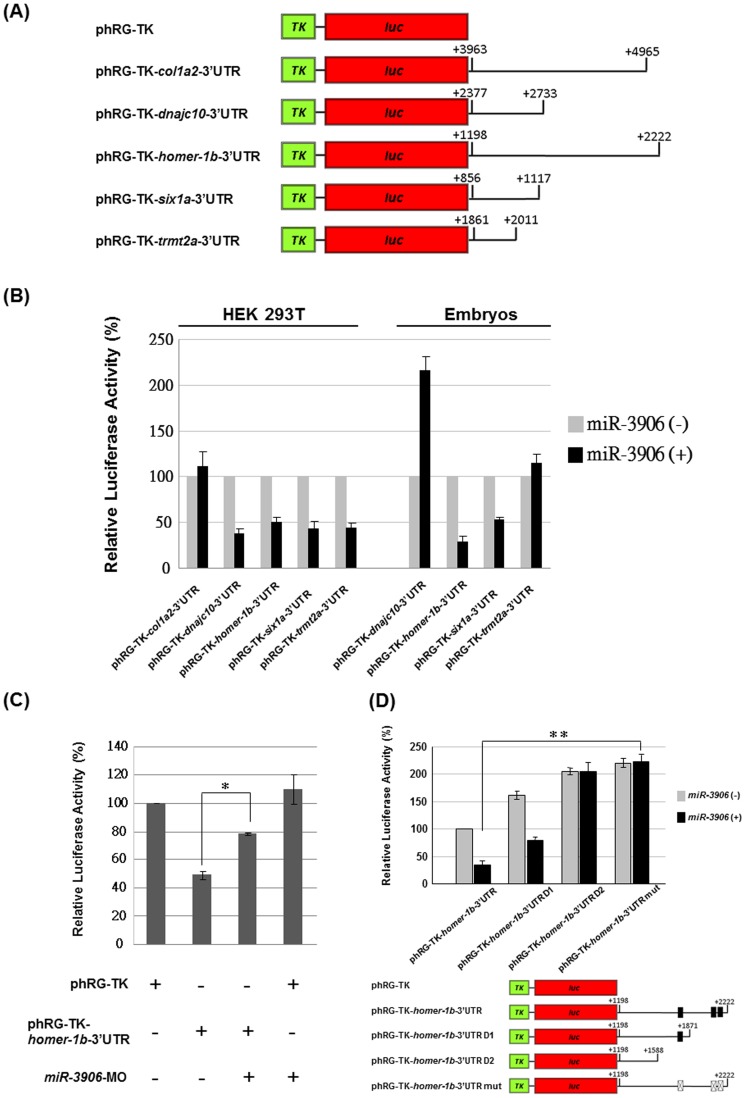
Figure 1. Luciferase (luc) activity assay of miR-3906 co-injected with plasmid constructs containing 3′UTR segment of putative miR-3906-target genes.
(A) Constructs for examining luc assay. The complete 3′UTR segments of col1a2, dnajc10, homer-1b, six1a and trmt2a, which are putative target genes of miR-3906, were ligated into the downstream of luc reporter gene contained in plasmid phRG-TK. (B) Plasmid pCMV-RFP-miR-3906 [miR-3906 (+)], a RFP reporter fused with pre-miR-3906 and driven by CMV promoter, was co-transfected with pGL3-TK (internal control) and each examined construct, as indicated, into HEK 293T cells. Injection of pGL3-TK and each examined construct without containing pCMV-RFP-miR-3906 [miR-3906 (−)] served as a control group, and its luc activity was 100%. In zebrafish embryos, we co-injected synthetic pre-miR-3906 RNA [miR-3906 (+)], pGL3-TK (internal control) and each examined construct in the experimental group. Injection of pGL3-TK and each examined construct without containing pre-miR-3906 RNA [miR-3906 (−)] served as control group, and its luc activity was 100%. Data were presented as means±SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). (C) Injection of plasmid phRG-TK, in which luc expression was driven by thymidine kinase (TK), served as a control, and its luc activity was 100%. The relative luc expression level of each combination, as indicated, was examined. All data were presented as means±SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). (D) Various lengths of 3′UTR segment derived from homer-1b mRNA (from 1198 to 2222 nt) fused with luc reporter gene and driven by TK promoter were constructed as indicated. Plasmid alone or plasmid plus pre-miR-3906 were individually injected in zebrafish embryos to perform luc assay. Data were presented as means±SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). Student's t-test determined significant differences between each group, and * indicates that the difference was significant at P<0.05. (black box: miR-3906-target sequences; cross filled box: miR-3906-target mutated sequences).