Figure 1.
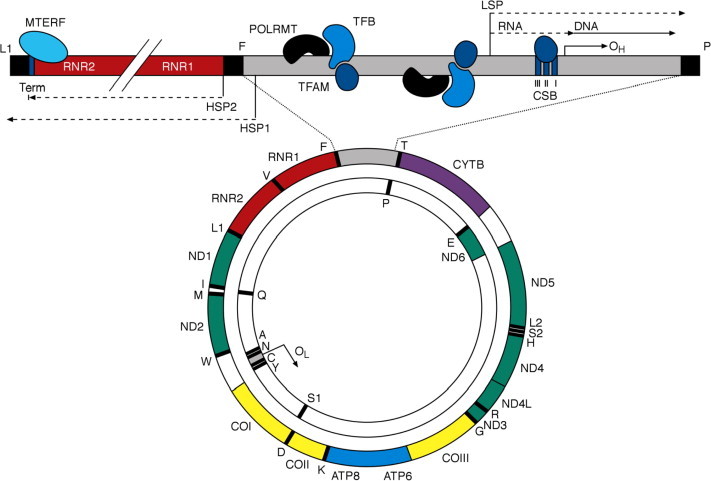
The human mitochondrial genome. Represented is a schematic diagram of the 16.6 kb circular, double-stranded human mitochondrial genome with an enhanced, linearised view of the D-loop and transcription termination regions. The outer circle represents the heavy (H) strand of the genome and the inner circle the light (L) strand. Human mtDNA encodes the two mt-rRNA genes (shown in red) RNR1 (12S rRNA) and RNR2 (16S rRNA), 22 mt-tRNAs (black bars) identified by their single letter abbreviation, and 13 essential respiratory chain polypeptides: seven subunits (ND1–ND6 and ND4L) of complex I (green), CYTB of complex III (purple), three catalytic subunits (COI–COIII) of complex IV (yellow) and ATP6 and ATP8 of complex V (blue). Major non-coding regions of the genome (grey) include the origin of L-strand replication (OL) and the 1.1 kb D-loop in which the origin of H-strand replication (OH) and regulatory elements and binding sequences for key factors involved in mtDNA transcription initiation and termination are located.
