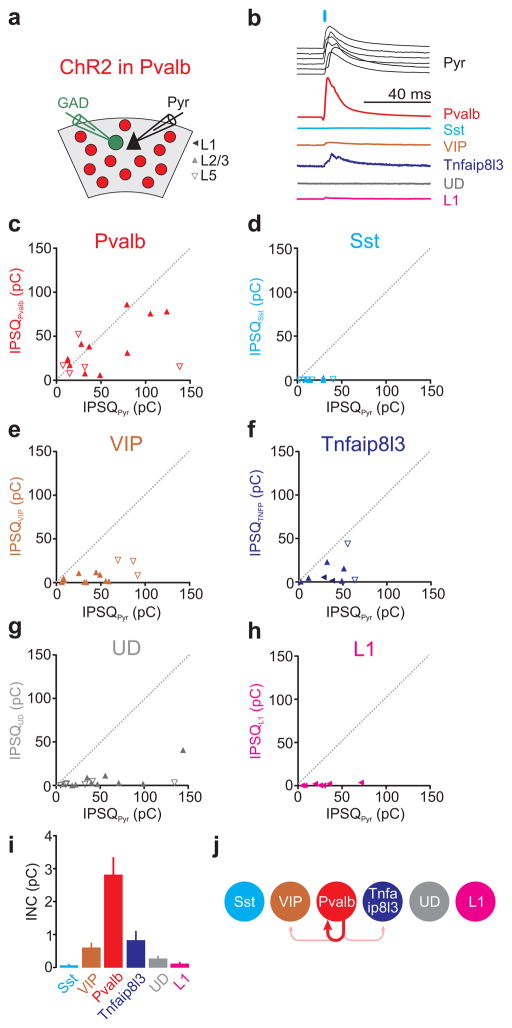
Figure 4. Pvalb cells mainly inhibit one another.
a) Schematic of experimental configuration: ChR2 expressing Pvalb-Cre cells are photo-stimulated while recording from a pyramidal cell (Pyr) and a neighboring GAD65/67 positive inhibitory neuron expressing GFP.
b) Example IPSCs simultaneously recorded in the reference pyramid (black) and in one of the six different interneuron categories (different colors). The order of the six pyramid IPSCs (top to bottom) matches the order of the IPSC simultaneously recorded in each of the six interneuron categories. For simplicity, all traces were scaled such that the pyramid IPSCs have the same peak amplitude.
c–h) The inhibitory postsynaptic charge (IPSQ) evoked by Pvalb cell photostimulation and recorded in individual interneurons (IPSQIN; y-axis) is plotted against the IPSQ simultaneously recorded in a pyramidal cell (IPSQPyr; x-axis; see (a) for symbol legend). Dotted line is unity line. Category(n of cells/slices/mice): Pvalb(16/15/10), Sst(9/9/6), VIP(15/12/9), Tnfaip8l3(9/5/5), Undefined-UD(16/12/9), L1(7/5/5).
i) Panel showing mean±s.e.m of individual neuronal contributions (INC) of all recorded pairs of the respective category. Note that Pvalb cells receive most inhibition.
j) Schematic illustration of the inhibition mediated by Pvalb cells onto each interneuron category (abbreviation as in Fig. 2e).