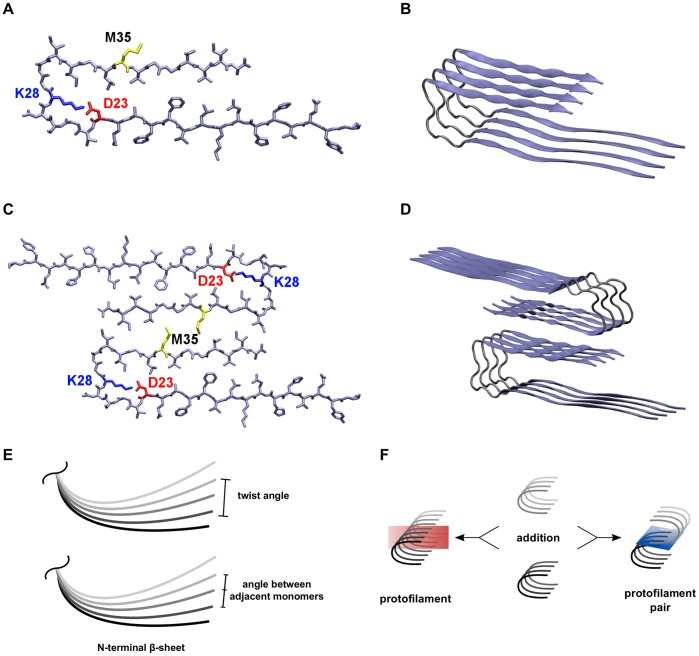
Figure 1. Presentation of the system and explanation of calculations.
(A) The orientation of sidechains in the protofilament monomer with the salt bridge between residues D23 (red) and K28 (blue), and residue M35 (yellow) of the C-terminus pointing towards the surrounding solvent. (B) The 4-mer (O ) as an example for the orientation of peptide chains within the protofilaments. (C) The interaction between hydrophobic residues around M35 (yellow) in the C-termini of two opposite protofilaments constitutes the interface in the protofilament pairs. (D) The 8-mer (O
) as an example for the orientation of peptide chains within the protofilaments. (C) The interaction between hydrophobic residues around M35 (yellow) in the C-termini of two opposite protofilaments constitutes the interface in the protofilament pairs. (D) The 8-mer (O ) as an example for the orientation of peptide chains in the protofilament pairs. (E) Two different angles were analyzed, the twist angle and the angle between adjacent monomers. (F) Two oligomers can either be combined to form a longer protofilament (elongation) or be merged via C-terminal contacts to form a protofilament pair (thickening). Therefore, two types of MM/GBSA calculations were performed: segmentation of protofilaments along the red plane and segmentation of protofilament pairs along the blue plane.
) as an example for the orientation of peptide chains in the protofilament pairs. (E) Two different angles were analyzed, the twist angle and the angle between adjacent monomers. (F) Two oligomers can either be combined to form a longer protofilament (elongation) or be merged via C-terminal contacts to form a protofilament pair (thickening). Therefore, two types of MM/GBSA calculations were performed: segmentation of protofilaments along the red plane and segmentation of protofilament pairs along the blue plane.