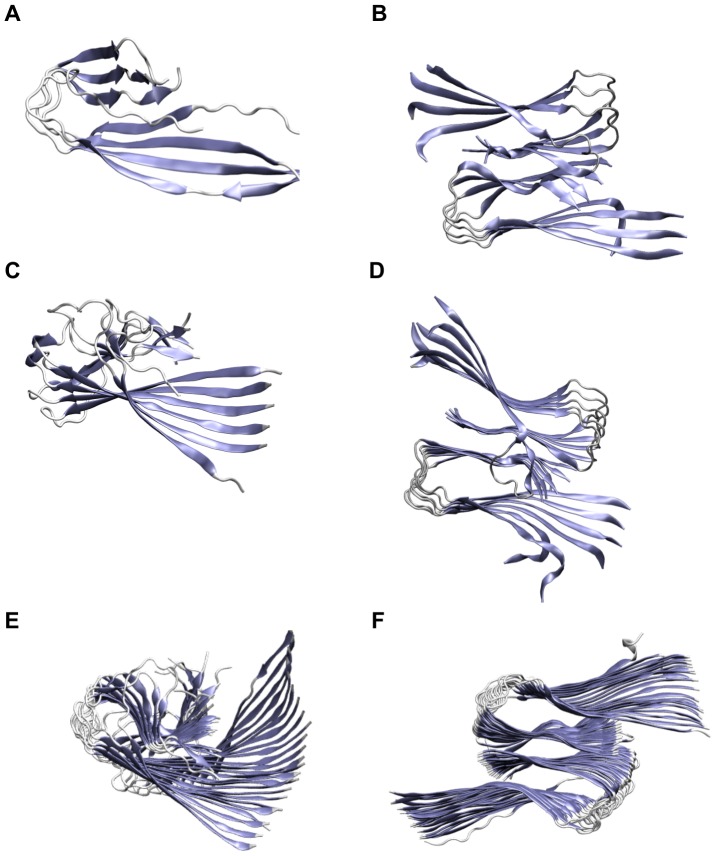
Figure 3. Final structures of the simulations of a small, medium, and large protofilament and its corresponding protofilament pair.
(A) The protofilament tetramer (O4) reveals a large twist angle and a flexible hinge region in the C-terminus. (B) The protofilament pair octamer (O2×4) shows a similar twist angle to the O , but the hydrophobic residues in the C-terminus are covered by the second layer. (C) The protofilament hexamer (O
, but the hydrophobic residues in the C-terminus are covered by the second layer. (C) The protofilament hexamer (O ) displays the large twist of the parallel
) displays the large twist of the parallel 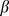 -sheets. (D) The protofilament pair dodecamer (O
-sheets. (D) The protofilament pair dodecamer (O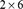 ) has a smaller twist angle than the protofilament hexamer due to the conteracting stabilization by the C-terminal interaction. (E) The protofilament 24-mer (O
) has a smaller twist angle than the protofilament hexamer due to the conteracting stabilization by the C-terminal interaction. (E) The protofilament 24-mer (O ) shows a small angle between adjacent monomers but the large overall twist angle. (F) The protofilament pair 48-mer (O
) shows a small angle between adjacent monomers but the large overall twist angle. (F) The protofilament pair 48-mer (O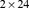 ) shows that the overall twist angle is reduced upon C-terminal interaction.
) shows that the overall twist angle is reduced upon C-terminal interaction.