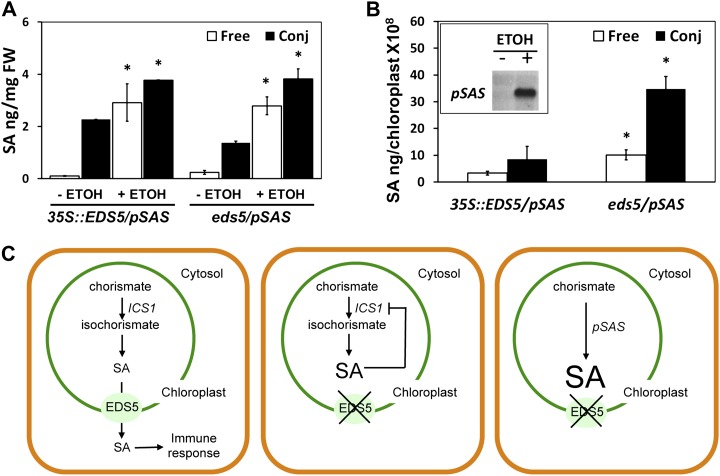
Figure 5.
Free and conjugated SA accumulate in the chloroplasts of eds5 mutants overproducing SA. SA content in 35S::EDS5 plants and eds5 mutants were both transformed with ALC::pSAS. A, Free and conjugated SA content in leaves 0 and 24 h after treatment with ethanol. Significant differences (Student’s t test; P < 0.05) of means ± sd (n = 4) from non-ethanol-induced plants are indicated by asterisks. FW, Fresh weight. B, Free and conjugated SA content in isolated chloroplasts 24 h after treatment with ethanol. The inset shows the expression of ALC::pSAS in leaves of transgenic plants after ethanol treatment. Significant differences (Student’s t test; P < 0.05) of means ± sd (n = 4) from 35S::EDS5 plants are indicated by asterisks. C, Model of EDS5 action. Left, the functional EDS5 (in either 35S::EDS5 or wild-type plants induced by biotic or abiotic stress) exports SA made in the chloroplast. Middle, in eds5 mutants, SA accumulates in the chloroplast and presumably shuts down its own biosynthesis by a negative feedback that has yet to be characterized in detail. Right, in eds5 mutants induced to express pSAS, SA accumulates in the chloroplasts.