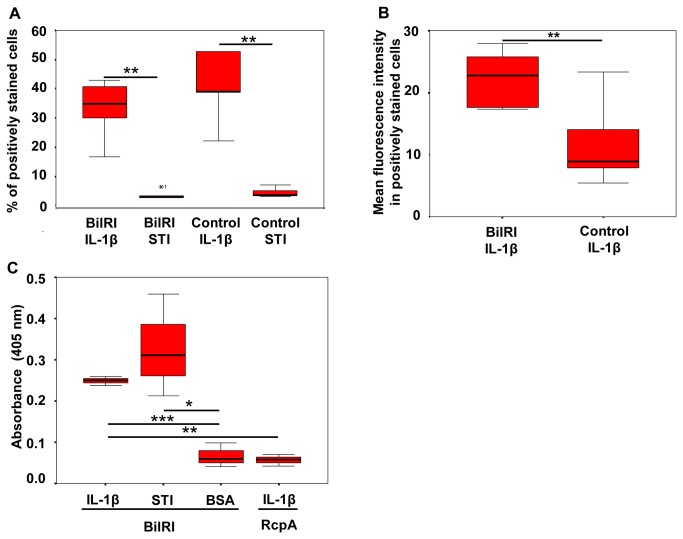
Figure 5. Recombinant BilRI bound IL-1β both in the outer membrane of E. coli and as soluble protein.
The IL-1β-binding capacity of recombinant E. coli cells containing BilRI in the outer membrane was studied using the Fluorokine™ assay (R&D Systems) and a flow cytometer. A similar number of the IPTG-induced cells bound IL-1β compared to non-induced cells (A). Neither group of cells showed significant binding of the control soybean trypsin inhibitor (STI) protein (A). However, the IPTG-induced recombinant E. coli cells bound IL-1β more efficiently than the non-induced cells, with the former showing a higher mean fluorescence intensity per positively stained cell than latter (B). When BilRI was expressed in E. coli without its signal sequence and purified from the cytoplasm, the obtained protein bound more efficiently to IL-1β than to BSA in a microplate assay (C). However, BilRI bound to IL-1β as efficiently as to STI (C). The negative outer membrane control protein from A. actinomycetemcomitans (the N-terminal portion of RcpA [32]) did not bind to IL-1β in the microplate assay (C). N=5 (A and B), and N=3-8 (C). Statistically significant differences are indicated as follows: * p≤0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001 (Paired T-test).