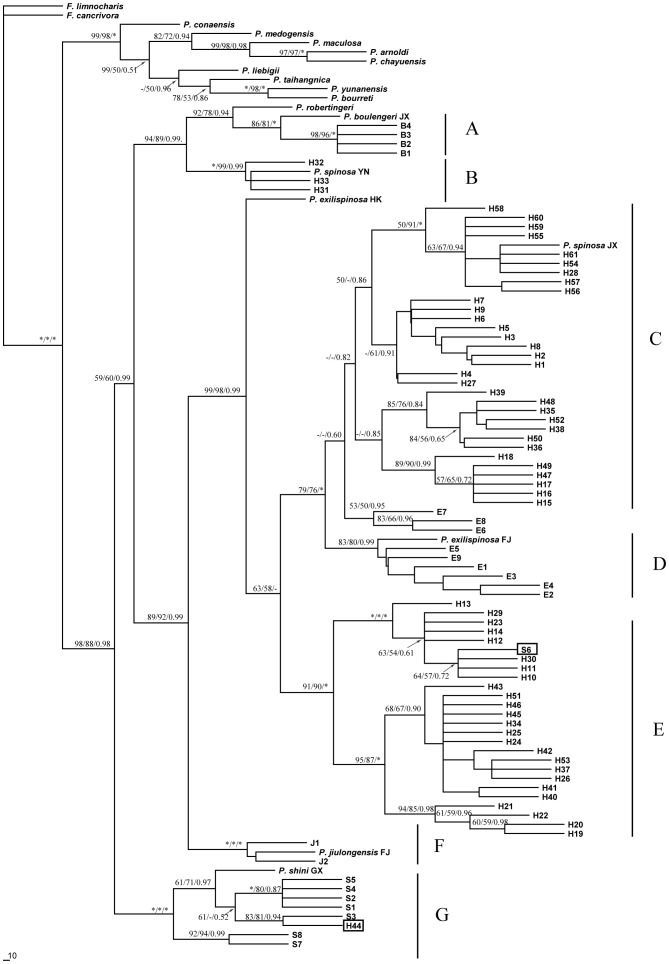
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationships of haplotypes, geographic distribution, and frequency of each Paa haplotype.
Phylogenetic relationships of haplotypes based on the 12S and 16S gene sequences, as determined by MP, ML, and Bayesian inference. Numbers above and below the branches are Bootstrap support values and Bayesian posterior probabilities ≥50 are indicated by the nodes. Legend: asterisk (“*”) indicates 100% ML and MP bootstrap support and 1.0 Bayesian posterior probabilities. “B,” haplotypes of P. boulengeri; “H,” haplotypes of P. spinosa; “J,” haplotypes of P. jiulongensis; “E,” haplotypes of P. exilispinosa; “S,” haplotypes of P. shini. P. spinosa YN and P. spinosa JX, sequences of P. spinosa obtained from GenBank; P. exilispinosa HK and P. exilispinosa FJ, sequence of P. exilispinosa obtained from GenBank; P. jiulongensis FJ, sequence of P. jiulongensis obtained from GenBank; P. shini GX, sequence of P. shini obtained from GenBank; P. taihangnica, P. liebigii, P. conaensis, P. medogensis, P. maculosa, P. arnoldi, P. chayuensis, P. robertingeri, P. yunanensis, P. bourreti, sequence of P. taihangnica, P. liebigii, P. conaensis, P. medogensis, P. maculosa, P. arnoldi, P. chayuensis, P. robertingeri, P. yunanensis, P. bourreti obtained from GenBank respectively.