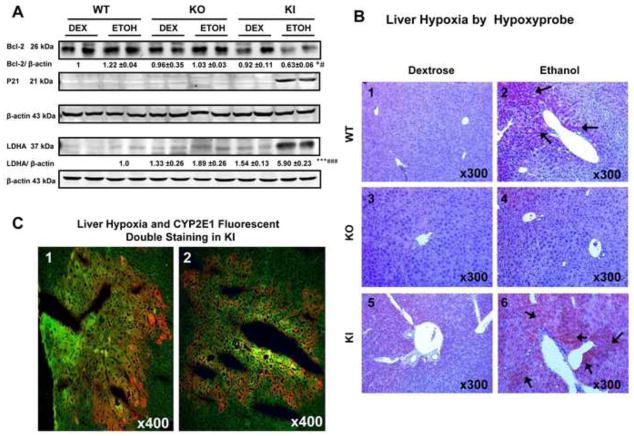
Fig. 4. Levels of HIF-1α Downstream Targets and Pimonidazole Staining After Chronic Ethanol Feeding.
(A) The levels of Bcl-2, P21 and LDHA protein. Levels of p21 were very low and could not be reproducibly detected except for the ethanol-fed KI mice. Levels of LDHA could not be reproducibly detected in the dextrose-fed WT mice. The ratio of LDHA/β-actin for the ethanol-fed WT mice was taken as 1.0, to be compared to the other groups. (B) Immunohistochemical staining of the hypoxia-marker pimonidazole in liver. Panel 4B6 shows strongly hypoxia positive staining in liver of the KI mice (+++) (arrows, IHCx300). Panel 4B2 shows hypoxia positive staining in WT mice (+) (arrows, IHCx300) fed with ethanol. Panel 4B4 or 4B1,4B3,4B5 show no positive staining in the KO mice (−) fed with ethanol or in any of the dextrose-fed mice. (C) Fluorescent double staining of hypoxia-specific pimondazole and CYP2E1 in hepatic centrilobule. Panels 1 and 2 show co-location (yellow) of hypoxia (yellowish green, IHCx400) and CYP2E1 (red, IHCx400) in the same centrilobular area of the liver in the KI mice fed with ethanol * p< 0.05, *** P <0.001 compared to the CYP2E1 KI groups fed dextrose. # p<0.05, ### p< 0.001 compared to CYP2E1 KO or WT groups fed ethanol or dextrose.