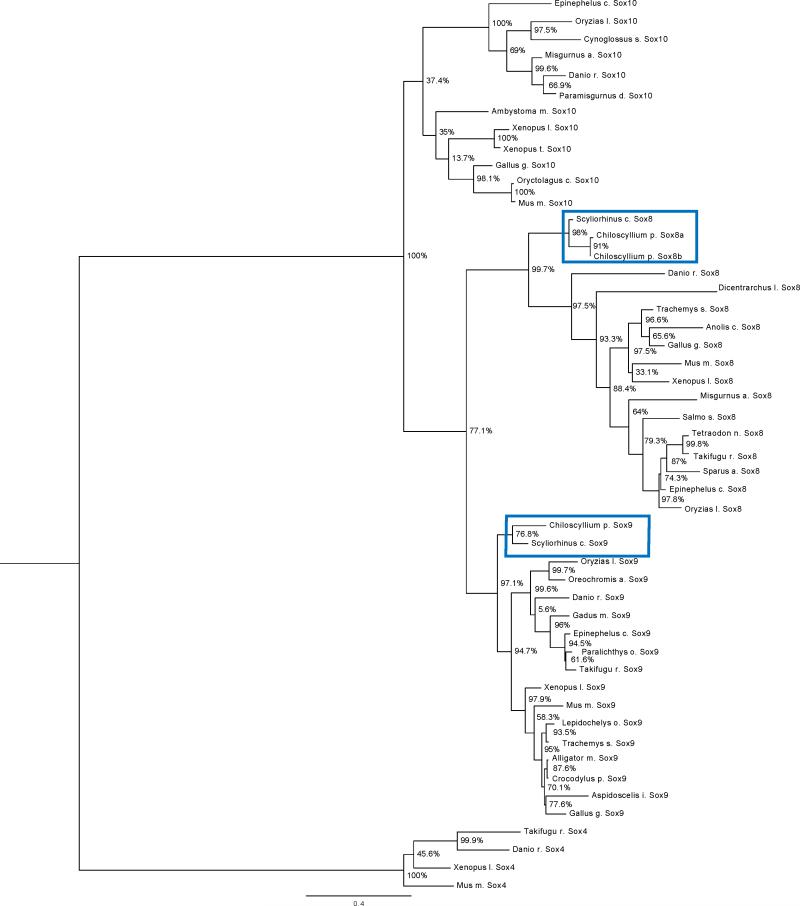
Figure 5. Rooted phylogenetic tree for Sox8, Sox9 and Sox10 HMG domains.
The rooted phylogenetic tree was obtained from the Nearest-Neighborhood Interchanges program performed on FastTree. The Sox8, Sox9 and Sox10 HMG domain protein sequences were found in various vertebrate species and used in construction of the tree. The bar range located on the bottom of the rooted phylogenetic tree represents the branch length of 0.4 units. The branch length is proportionally related to the evolutionary distances and reflects the divergence between the Sox8, Sox9 and Sox10 genes. The unbiased SH test values are indicated on the branch nodes as percent similarities between the clades. The outgroup used was Sox4, which is part of the SoxC sub-family. C. punctatum Sox8 and Sox9 clones were positioned at the beginning of the phylogenetic tree indicating that our C. punctatum clones are more ancient than the rest of vertebrates with Sox8, Sox9 and Sox10 sub-families.