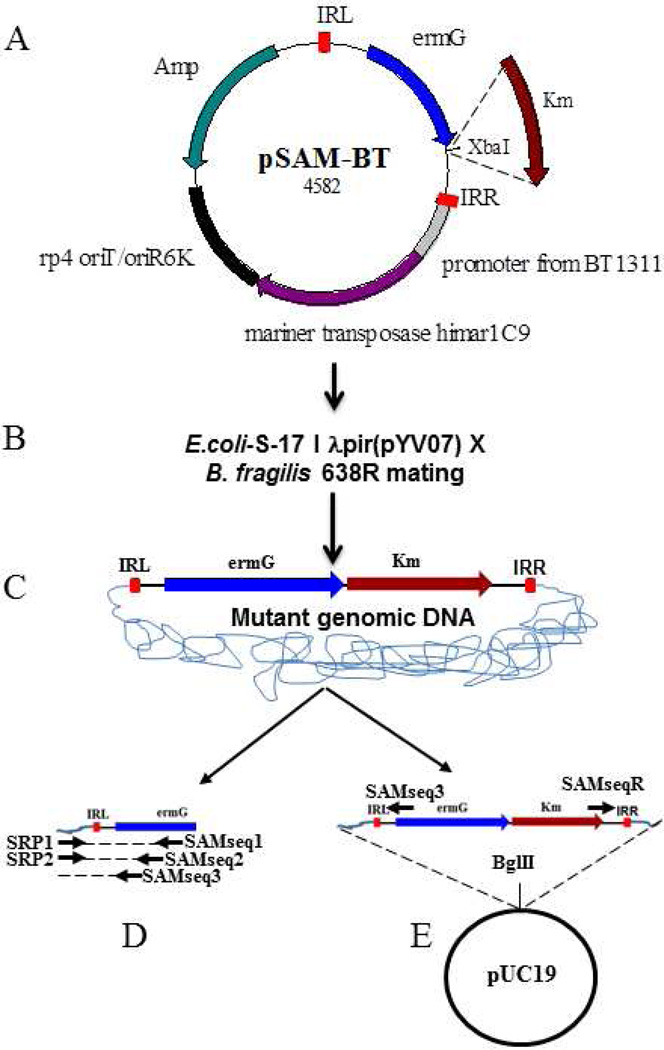
Fig. 1.
Transposon mutagenesis of B. fragilis 638R. A) The mariner transposon vector pSAM-Bt. IRL, Inverted repeat left; ermG-provides erythromycin resistance in B. fragilis; rp4 oriT/oriR6K-conditional origin of replication facilitates plasmid replication only in E. coli; Amp-ampicillin resistance gene for E. coli. Plasmid pYV07 was created by cloning Km-kanamycin resistance gene at the XbaI site of pSAM-Bt. B) Transposon mutants are generated by mating E. coli S-17 λ pir-pYV07 with B. fragilis 638R. C) When pYV07 enters B. fragilis 638R, the mariner transposase, whose expression is driven by B. thetaiotaomicron promoter (BT1331), inserts the transposon DNA (ie. IRL, ermG, Km and IRR) into the genome. The transposon mutants become resistant to erythromycin. D) Transposon disrupted gene identification by SRP-PCR and E) Transposon disrupted gene identification by rescue cloning. Mutant genomic DNA can be cut with BglII and cloned into BglII-digested pUC19. Sequencing with SAMseq3 and SAMseqR primer yields transposon junction DNA.