Figure 3.
Septins Inhibit Cdc42 Activity in a GAP-Dependent Negative Feedback Loop
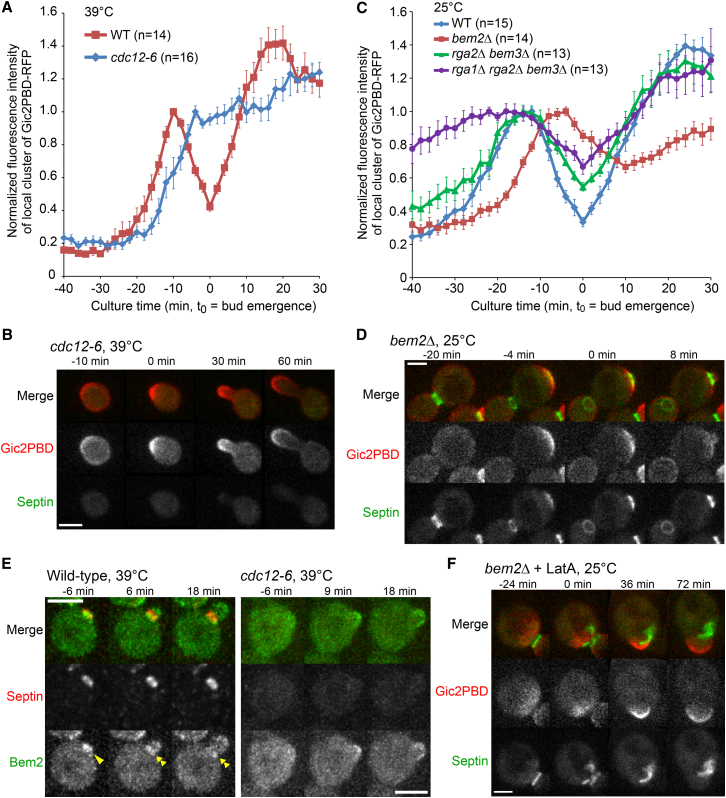
(A) Negative-feedback regulation of Cdc42 requires septins. Gic2PBD intensity was quantified using a threshold method as in Figure 1B. Each point indicates average fluorescence intensity of Gic2PBD. Error bars represent SEM.
(B) Hyphae-like polarized growth in a septin mutant cdc12-6. See also Figure S4.
(C) Inhibition of Cdc42 activity depends on Cdc42 GAPs. Gic2PBD intensity was quantified using a threshold method as in Figure 1B. Each point indicates average fluorescence intensity of Gic2PBD. Error bars represent SEM.
(D) Large Cdc42 clusters and wide septin rings formed in a Cdc42 GAP mutant (bem2Δ). See also Figure S4 and Movie S1.
(E) Bem2 associates with septins at the PBS prior to bud emergence (single arrowhead) and with the septin ring afterward (double arrowheads). The localization of Bem2 at the bud neck, not the bud cortex, is fully dependent on septins (right panel).
(F) Broad shmoo-like protrusions in latA-treated bem2Δ cells. See also Movie S2.
Scale bars represent 3 μm.