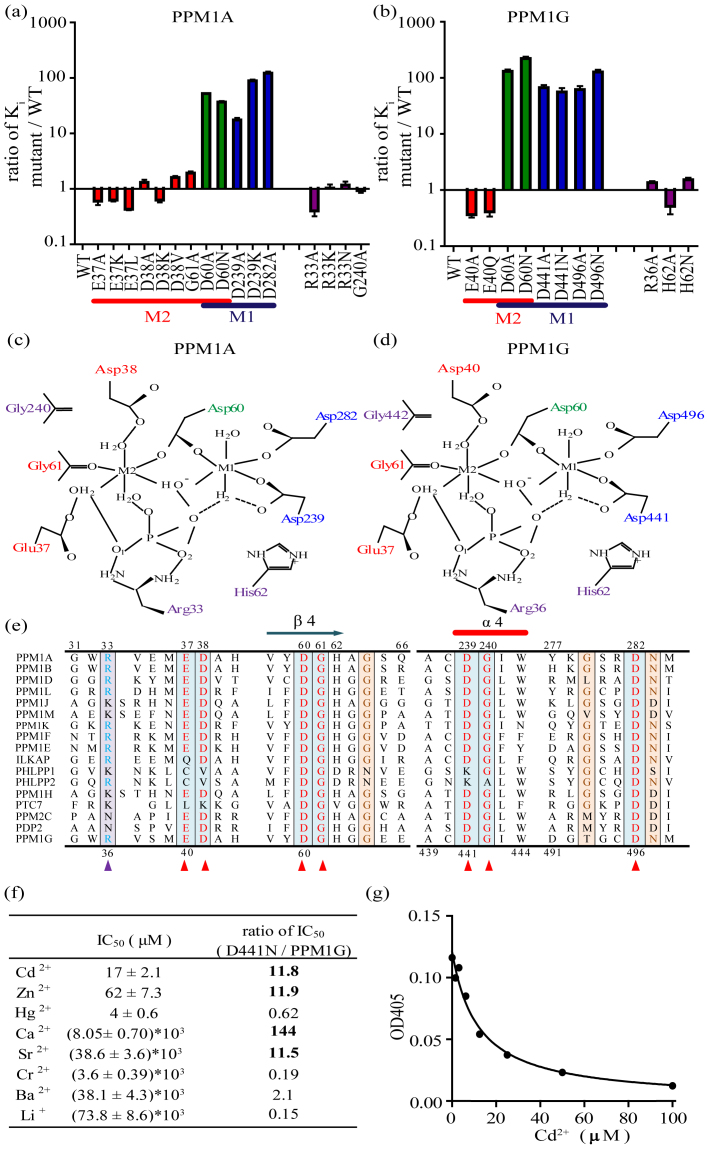
Figure 3. Cadmium inhibits PPM1A and PPM1G through the M1 metal ion binding site.
(a–b) Column graph of the Ki values of Cd2+ for the wild-type enzymes and the PPM1A and PPM1G mutants. All assays were performed in Tris/Bis-Tris/acetate buffer with Mn2+ as the variable substrate at saturating levels of pNPP. Colors: Residues that exclusively coordinate with the M2 metal binding site are red, residues that exclusively coordinate with the M1 metal binding site are blue, and residues shared by the M1 and M2 sites are green. Residues not associated with the metal ion centers are purple. (c–d) Schematic representation of the active center of human PPM1A and PPM1G based on the X-ray crystal structure reported by Das et al22. (e) Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of human PPM1A and PPM1G with the signature sequence motifs of all other members of the PPM family in humans. The amino acids of PPM1A and PPM1G are numbered on the top and bottom, respectively. The residues that bind to the metal ions or phosphate ions are shown in red and blue, respectively. (f) IC50 values of different divalent metal ions for the inhibition of the PPM1G D441N mutant and their relative ratio compared with wild-type PPM1G. (g) Concentration-dependent inhibition of D441N activity on pNPP by Cd2+.