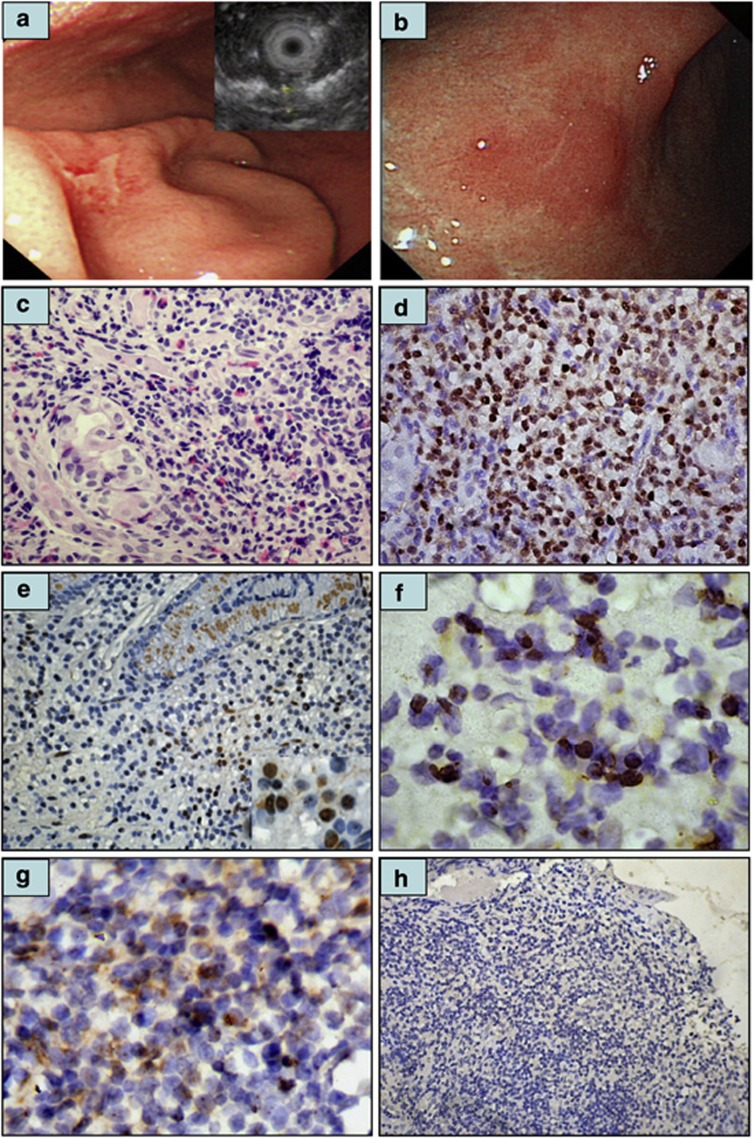
Figure 1.
Immunohistochemical analysis of CagA expression in tumor cells of gastric MALT lymphoma. (a) Endoscopy showing irregular shallow ulcers in the greater curvature of the lower body of the stomach in a 43-year-old man (right top inset: thickness of mucosa 3.6 mm in endoscopic ultrasonography). (b) One month after the completion of HPE, complete regression of all diffuse ulcerations with hyperemic and atrophic mucosa in the lower body of the stomach. (c) Histopathologic examination of the same case revealing diffuse infiltration of small lymphoid cells containing angulated nuclei and pale clear cytoplasm. Lymphoepithelial lesion is also discernible. (d) Tumor cell nuclear CagA expression in the same case (c). (e) An H. pylori-dependent case (time to pCR after HPE, 3 months) displaying nuclear CagA expression in the tumor cells of the gastric mucosa (right bottom inset, × 1000). (f) An H. pylori-dependent case (time to pCR after HPE, 11 months) displaying nuclear CagA expression in the tumor cells of gastric submucosa ( × 1000). (g) An H. pylori-dependent case displaying cytoplasmic CagA expression in the tumor cells of gastric submucosa (time to pCR after HPE, 16 months). (h) Absence of CagA expression in the tumor cells of an H. pylori-independent case.