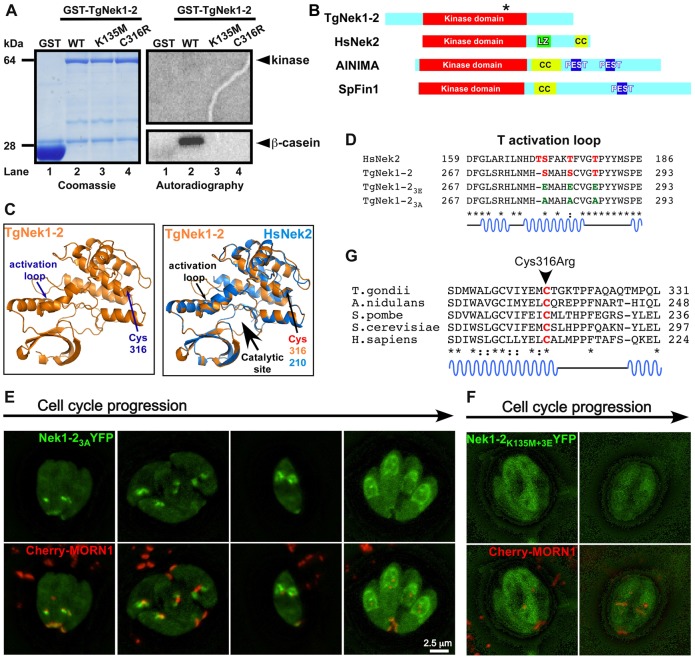
Fig. 6.
Examination of TgNek1-2 kinase activity. (A) In vitro kinase assay using GST-TgNek1-2. Recombinant GST (lane 1), GST-TgNek1-2 (lane 2), GST-TgNek1-2K135M (kinase dead; lane 3) and GST-TgNek1-2C316R (ts-mutant; lane 4) were expressed and purified from bacteria and incubated with β-casein. The results were analyzed by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and subjected to Coomassie staining and autoradiography. (B) Domain analysis of TgNek1-2 and HsNek2. Leucine zipper (LZ), coiled-coil (CC) and PEST domains are marked. The asterisk on TgNek1-2 indicates the Cys316Arg mutation. (C) Protein modeling of TgNek1-2 onto human Nek2 (Westwood et al., 2009). (D) Sequence alignment of T-loop in TgNek1-2 and HsNek2. Conserved and phosphorylated serine and threonines are marked in red. Glutamic acid and alanine substitutions in the activation loop mutants are shown in green. (E,F) Live cell images of transiently expressed TgNek1-23A-YFP (E) and TgNek1-2K135M+3E-YFP (F) driven by α-tubulin promoter in a line expressing Cherry-MORN1 show distinct localization patterns. (G) Alignment of the conserved region of TgNek1-2 containing the temperature-sensitive mutation in V-A15 with selected orthologs. Asterisks indicate conserved amino acids; dots indicate identical residues; colons indicate similar residues.