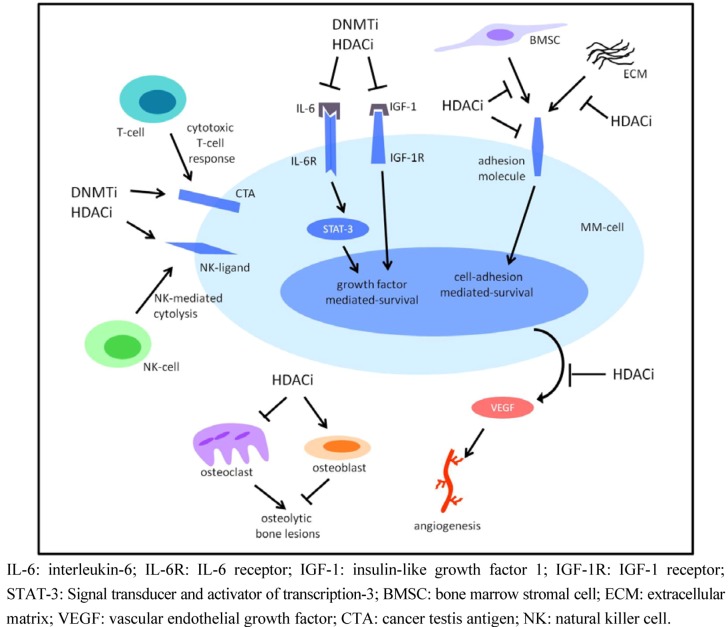
Figure 2.
HDACi and DNMTi target the BM microenvironment. HDACi and DNMTi affected several pathways in relation to the BM-microenvironment. Firstly, HDACi and DNMTi inhibit cytokine signaling by reducing expression of IGF-1R, IL-6R and IGF-1. In addition, HDACi decrease expression of adhesion molecules, thereby attenuating adhesion-mediated survival. HDACi also inhibit the expression and secretion of VEGF, thereby decreasing angiogenesis. Both HDACi and DNMTi upregulate CTAs and NK-ligands. This leads to an increased potential of cytotoxic T-cell responses and NK-mediated cytolysis. HDACi are furthermore shown to reduce osteoclast numbers and stimulate osteoblast generation, thereby inhibiting the development of osteolytic bone lesions.