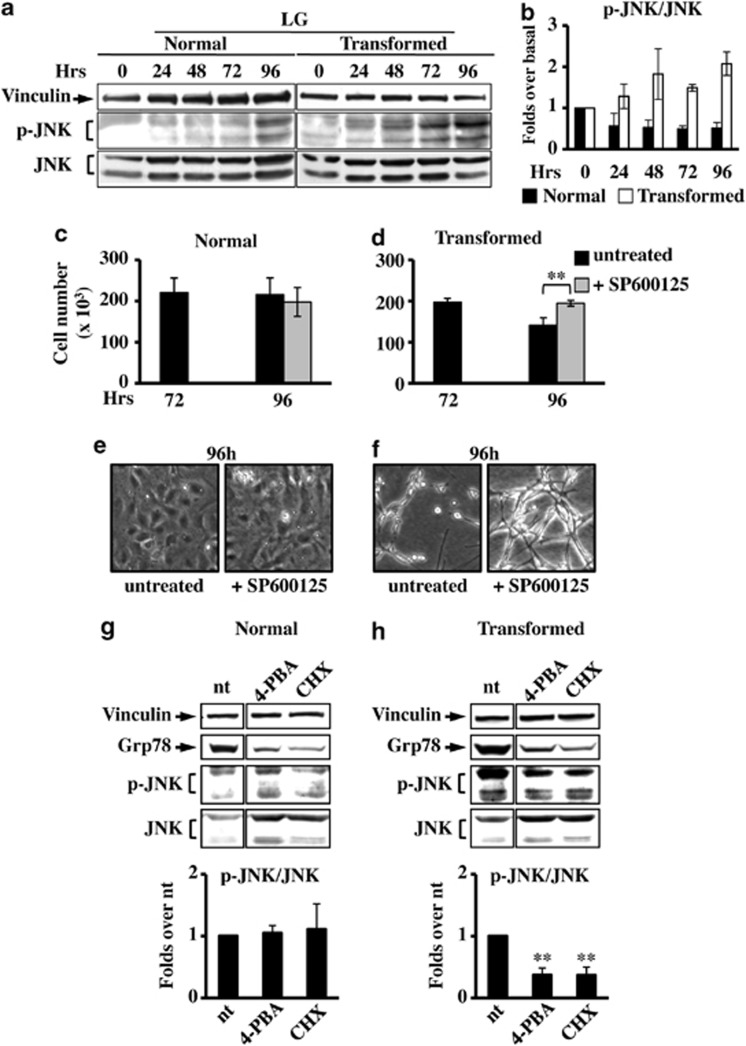
Figure 5.
JNK inhibition causes survival in transformed cells grown in LG. (a) For JNK expression analysis, normal and transformed cells, grown in LG, were collected at indicated time points and total cellular extracts were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by western blot analysis with antibodies anti-phospho-JNK Thr183/Tyr185 (p-JNK) and anti-total JNK. As loading control the expression of vinculin was analyzed. (b) Quantitative analysis of JNK phosphorylation status was performed by densitometric analysis of western blot films. The values obtained for P-JNK were normalized to the corresponding total JNK and vinculin values and plotted as fold changes over basal sample (0 h=1). Normal (c) and transformed (d) cells, grown in LG, were counted at 72 h and 96 h after 24 h of treatment with the JNK inhibitor, SP600125. Phase contrast microscopy images were collected for untreated and treated normal (e) and transformed (f) cells at 96 h of culture. All data represent the average of at least three independent experiments (±S.D.); **P<0.01, Student's t-test. (g and h) Analysis of p-JNK level in normal (g) and transformed (h) cells at 96 h of culture after 24 h of treatment with 4-PBA and CHX. The densitometric values for p-JNK, shown in the bottom histograms, were normalized as above and plotted as fold change over untreated (nt) sample. Data represent the average of at least three independent experiments (±S.E.M.); **P<0.01 as compared with nt, Student's t-test. UPR activation was followed through the expression analysis of Grp78 and as loading control the expression of vinculin was used