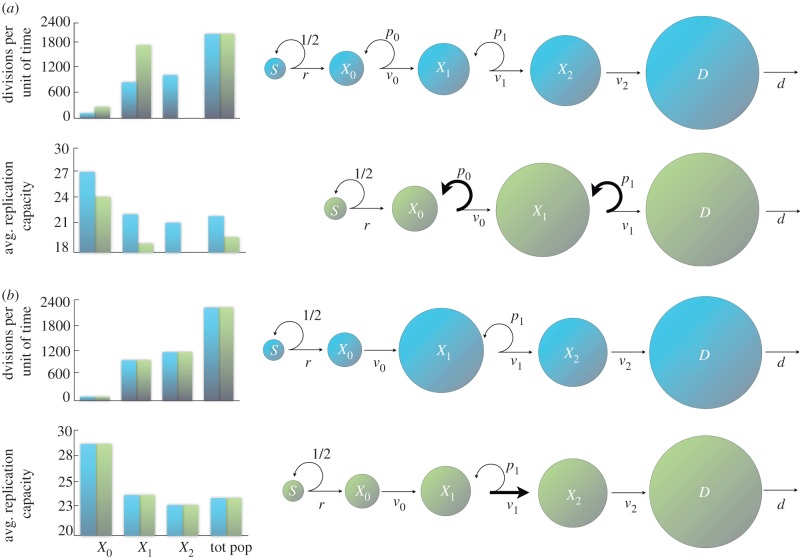
Figure 2.
Alternative architectures for the same target number of divisions in the intermediate cell population. (a) Increasing the self-renewal probability increases the size and the number of divisions per unit of time of a compartment. The same target number of divisions in the intermediate cell population can be reached by a lineage with smaller self-renewal probabilities and three intermediate compartments (blue), or by a lineage with larger self-renewal probabilities and only two intermediate cell compartments (green). The size of circles is indicative of population size. Bar plots: the average replication capacity and the number of divisions in the compartments depend on the architecture of the cell lineage. (See text for discussion.) In this case, rS = 50, dD = 2100 and all vi = 1. Blue parameters: (p0 = 0.3, p1 = 0.4, p2 = 0). Green parameters: (p0 = 0.41, p1 = 0.41). (b) An increase in the division rate of a compartment produces a decrease in the compartment's size; however, the number of divisions per unit of time and the average replication capacity in a compartment are independent of the division rate. Note that the number of divisions per unit of time increases with each compartment. (See text for discussion.) In this case, rS = 100, dD = 2400, p0 = 0, p1 = 0.4, p2 = 0, v0 = 1, v2 = 1.5 and k = 2. Blue parameters: (v1 = 1). Green parameters: (v1 = 2).