Figures 1–8.
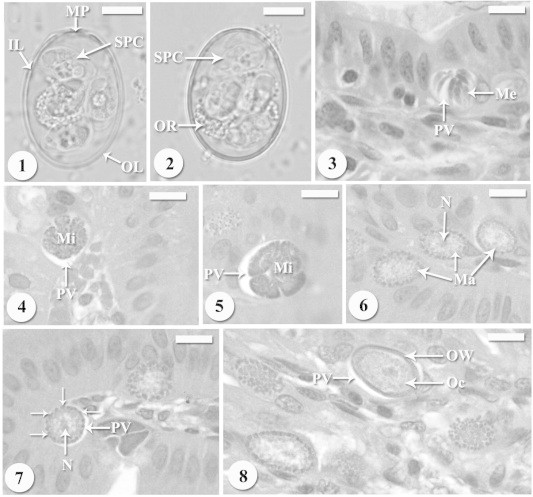
(1, 2) Light micrographs of freshly shed sporulated oocysts of Eimeria perforans collected from naturally infecting domestic rabbits Oryctolagus cuniculus. Oocyst has four sporocysts (SPC), oocyst residuum (OR), micropyle (MP) and surrounded by two membrane layers; outer layer (OL) and inner layer (IL). Scale-bar = 5 μm. (3) Mature meronts with mature merozoites (Me) in the parasitophorous vacuole (PV). Scale-bar = 10 μm. (4, 5) Developing microgamonts in bright parasitophorous vacuole (PV). Scale-bar = 10 μm. (6) Young macrogamonts with prominent nucleus and located in parasitophorous vacuole (PV). Scale-bar = 10 μm. (7) Developing macrogamonts with peripherally arranged wall-forming bodies (arrows) and prominent nucleus and located in parasitophorous vacuole (PV). Scale-bar = 10 μm. (8) Young oocyst (Oc) surrounded by the oocyst wall (OW) and located in parasitophorous vacuole (PV). Scale-bar = 10 μm.
