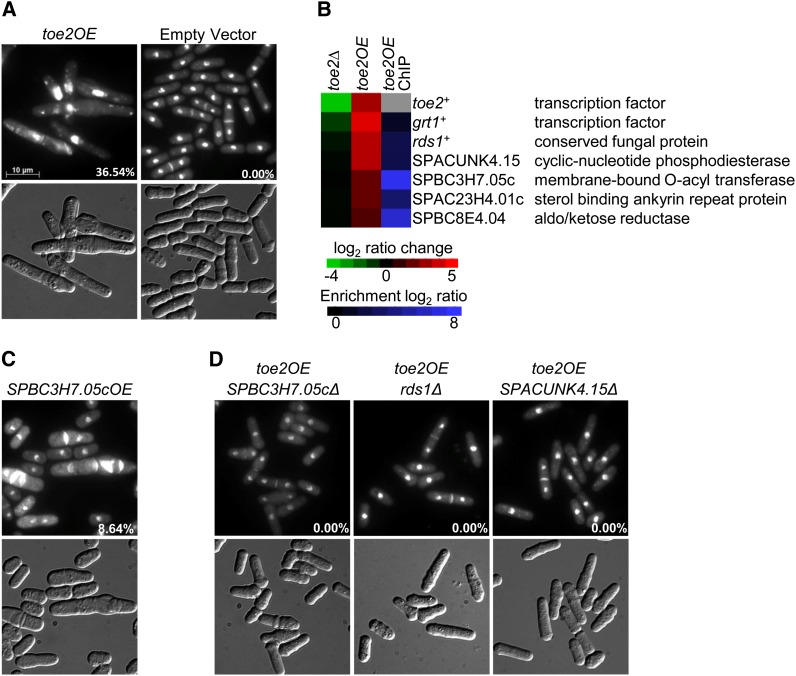
Figure 4.
Identification of Toe2 putative target genes by phenotypic activation. (A) Overexpression of toe2+ by the nmt1 promoter produces elongated cells that exhibit aberrant septal deposition. The toe2OE and empty vector strains were grown for 24 hr in EMM lacking thiamine medium at 30°. Cells were fixed with methanol and stained with DAPI and calcofluor white to visualize nuclei and cell-wall material, respectively (top panels). Cells are shown with Normarski in the bottom panels. (B) Putative target genes of Toe2 are induced in the nmt41-toe2OE-HA strain and are bound by Toe2 at their promoters. The heat map shows the relative expression of six putative target genes in the toe2Δ strain compared to wild type (left column) and the nmt41-driven toe2-HA strain compared to an empty vector control (middle column) by transcriptome profiling with dye reversal. The right column shows promoter occupancy of the putative target genes by Toe2 with ChIP-chip analysis of an nmt41-driven toe2-HA strain. The color bars indicate the relative expression and ChIP enrichment ratios between experimental and control strains. (C) Ectopic expression of the sequence orphan SPBC3H7.05c results in a similar aberrant septal deposition phenotype as seen in the toe2OE strain. The SPBC3H7.05cOE strain (nmt1-regulated) was cultured and prepared as described above. (D) The aberrant septal deposition phenotype of the toe2OE strain is abrogated by the single deletion of the putative target genes SPBC3H7.05c, rds1+, and SPACUNK4.15c. An nmt1-driven toe2+ was ectopically expressed in each of the three corresponding deletion backgrounds. These strains were prepared and stained as described above. The presence of the pREP1-toe2+ vector in these strains was confirmed by growth on selective medium as well as by PCR. Percentages indicate the proportion of cells exhibiting the septal defect.