Figure 2.
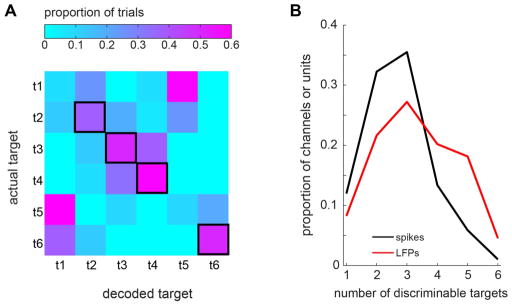
A. An example LFP channel which discriminated 4 reach targets. The matrix represents the 6-target decoding result from the example LFP channel. The color of each square represents the proportion of the trials for which the actual target corresponds to the row number and the decoded target corresponds to the column number. Each row is normalized such that the sum across the columns of each row is 1. The four squares with thick black borders indicate that a majority of trials in their corresponding row is decoded correctly, i.e., the actual target in each of those rows is discriminable. B. The distribution of the number of discriminable reach targets by single tuned LFPs or spike units.
