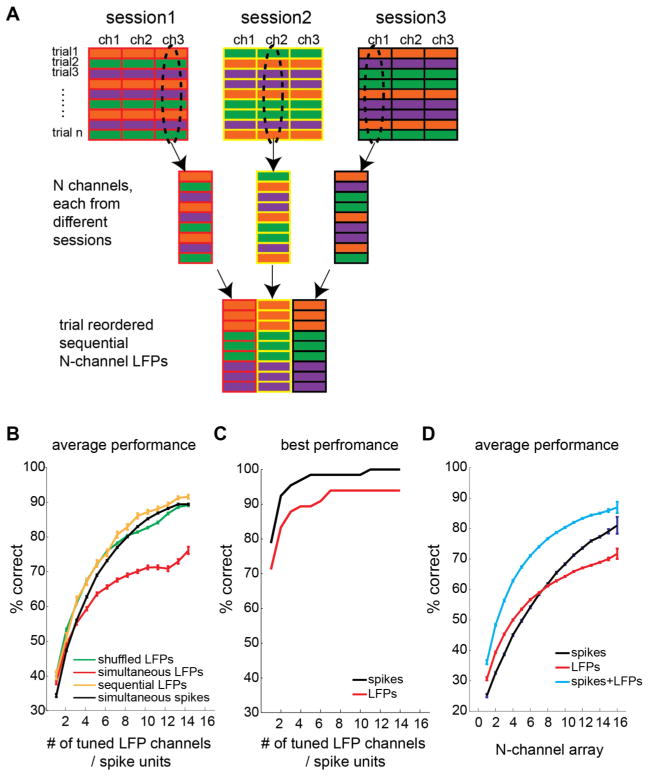
Figure 4.
A. The construction procedure for sequential multichannel LFPs. Each column represents a single channel. Each row represents a single trial. Different filling colors indicate different reach targets. A set of channels is selected from different sessions, and the trial sequences are reordered such that the selected channels have the same target sequence. B. The average decoding performance for each number of tuned LFP channels or tuned spike units, for the simultaneously recoded data, trial-shuffled data, and sequentially recorded data. C. The best decoding performance for each number of simultaneously tuned LFP channels or spike units. D. The average decoding performance for each number of simultaneously recorded electrodes, when using spike units, LFPs, and both signals. The error bars indicate the standard errors of means.