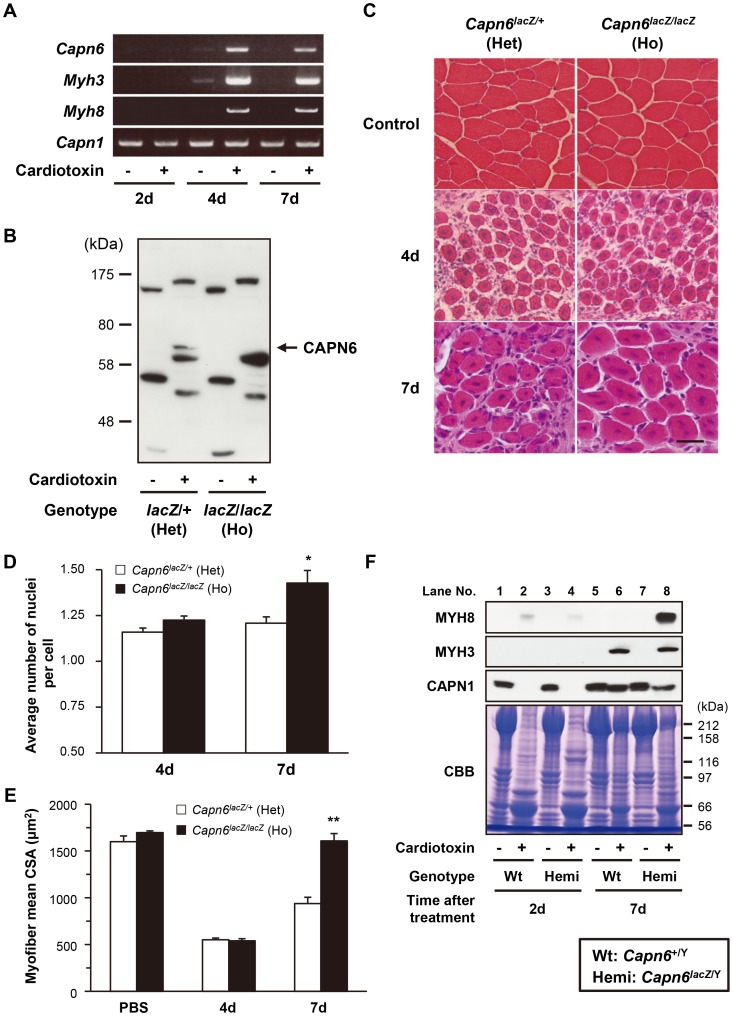
Figure 5. CAPN6 is expressed in regenerating skeletal muscles and suppresses regeneration.
(A) RT-PCR with total RNAs extracted from skeletal muscles of 7-wk-old wild-type mice 2 d, 4 d, and 7 d after cardiotoxin or PBS (control) injection. The PCR bands of Capn6 were amplified with the primers that detect full-length Capn6 mRNA. Myh3 and Myh8 mRNA was amplified to confirm that skeletal muscles successfully regenerated after their cardiotoxin-induced degeneration; Capn1 mRNA was detected as an internal control. (B) Western blot analysis using antibodies against CAPN6, of skeletal muscle lysates of 7-wk-old Capn6lacZ/+ and Capn6lacZ/lacZ mice, 5 days after cardiotoxin or PBS (control) injection. The specific CAPN6 band, indicated by an arrow, was detected around 70 kDa, and was not detected in Capn6lacZ/lacZ mice. (C–E) Histological analysis of the TA muscles of 7-wk-old Capn6lacZ/+ and Capn6lacZ/lacZ mice after a cardiotoxin or PBS (control) injection. Regenerating skeletal muscles with central nuclei were observed 4 d after the cardiotoxin injection. Remarkable degeneration was not observed in TA muscles at 4d after a PBS injection (shown as control) (C). Scale bar: 50 µm. Seven days after the injection, the average number of nuclei per cell was significantly greater in Capn6lacZ/lacZ (1.43 [mean]±0.06 [s.e.m.]) than in Capn6lacZ/+ (1.21±0.03) (D), and the mean CSA of the regenerating muscle myofibers was also significantly greater in Capn6lacZ/lacZ (1608.0 [mean]±78.5 [s.e.m.] µm) than in Capn6lacZ/+ (938.0±67.2 µm) (E). *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01 by Student's t-test. Each value is the mean from five experiments, and 50 cells were counted in each experiment. (F) Western blot analysis with skeletal muscle lysates of 7-wk-old Capn6lacZ/Y and Capn6+/Y mice 2d and 7 d after cardiotoxin or PBS (control) injection using antibodies against MYH3, MYH8 and CAPN1. CBB staining was used as an internal control. Wt, Capn6+/Y (♂); Hemi, Capn6lacZ/Y (♂); Het, Capn6lacZ/+ (♀); Ho, Capn6lacZ/lacZ (♀).