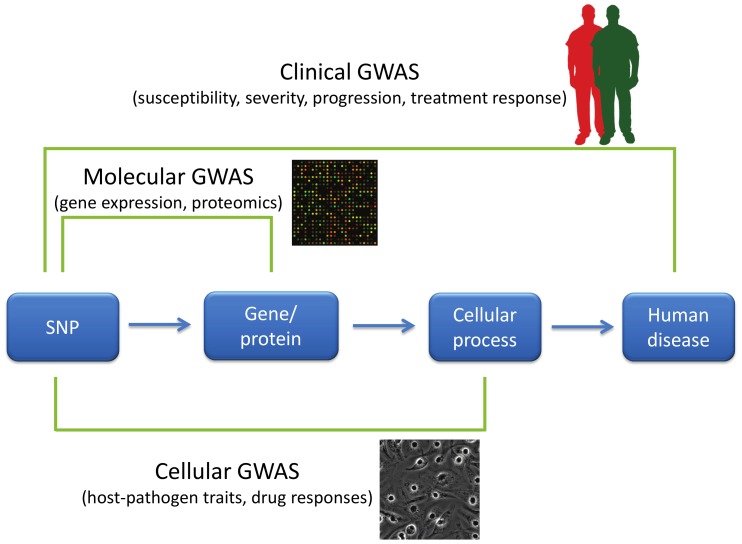
Figure 1. GWAS of varying phenotypic scales.
GWAS have primarily been used to characterize disease-related characteristics in patient populations, but new approaches have expanded the phenotypes used in GWAS. “Clinical GWAS” search for associations between genetic differences (primarily in the form of SNPs) and human disease traits such as disease risk, severity of disease, disease progression, and response to treatment. “Molecular GWAS” search for associations between SNPs and molecular phenotypes such as levels of mRNAs, proteins, or metabolites. Finally, “cellular GWAS” connect SNPs to particular cellular processes. Phenotypic variation in these cellular processes can be examined by manipulation either pharmacologically or using pathogens.