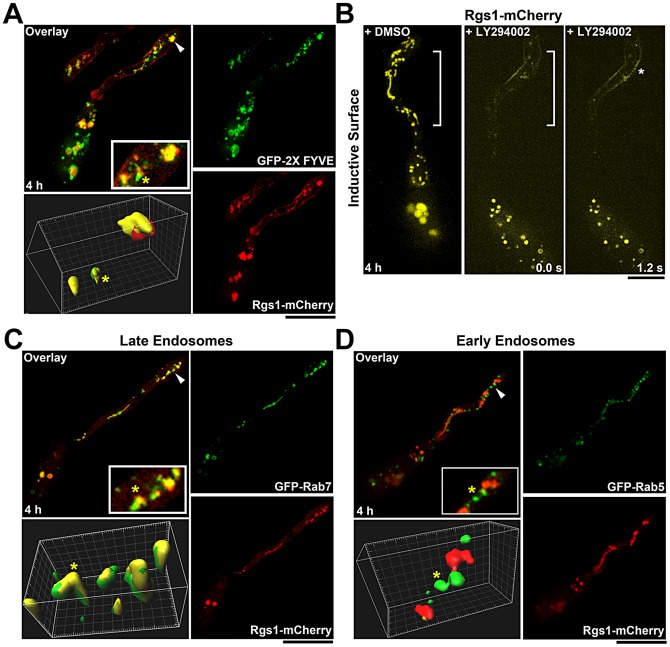
Figure 4. Identity and integrity of the tubulo-vesicular compartments that harbor Rgs1.
(A) Rgs1-mCherry colocalizes with certain PI3P-rich endosomal compartments (marked by GFP-FYVE probe). Arrowheads mark the regions magnified in the inset and surface rendered in 3D. (B) Inhibition of PI3 kinase activity by LY294002 results in the loss of Rgs1-mCherry (pseudocoloured yellow) association with tubulo-vesicular structures. Asterisk indicates Rgs1 accumulation along the plasma membrane of the incipient appressorium. DMSO treated sample was used a control. The regions of the germ tube lacking the Rgs1-mC compartments structures are bracketed. LY294002 treatment was carried out 4 hpi. The elapsed time is indicated in seconds (C) GFP-Rab7 colocalizes with Rgs1-mCherry during early stages of pathogenesis. The arrowhead depicts the region magnified in the inset and surface rendered in 3D. (D) The early endosomal marker Rab5 does not colocalize with Rgs1-mCherry. Arrowheads mark the regions magnified in the inset and surface rendered in 3D. Images are maximum intensity Z-projections of five confocal stacks (0.5 µm each) and the yellow asterisk, in the colocalization panels, marks the same compartment in the inset and the surface renderings. Scale bar, 10 µm.