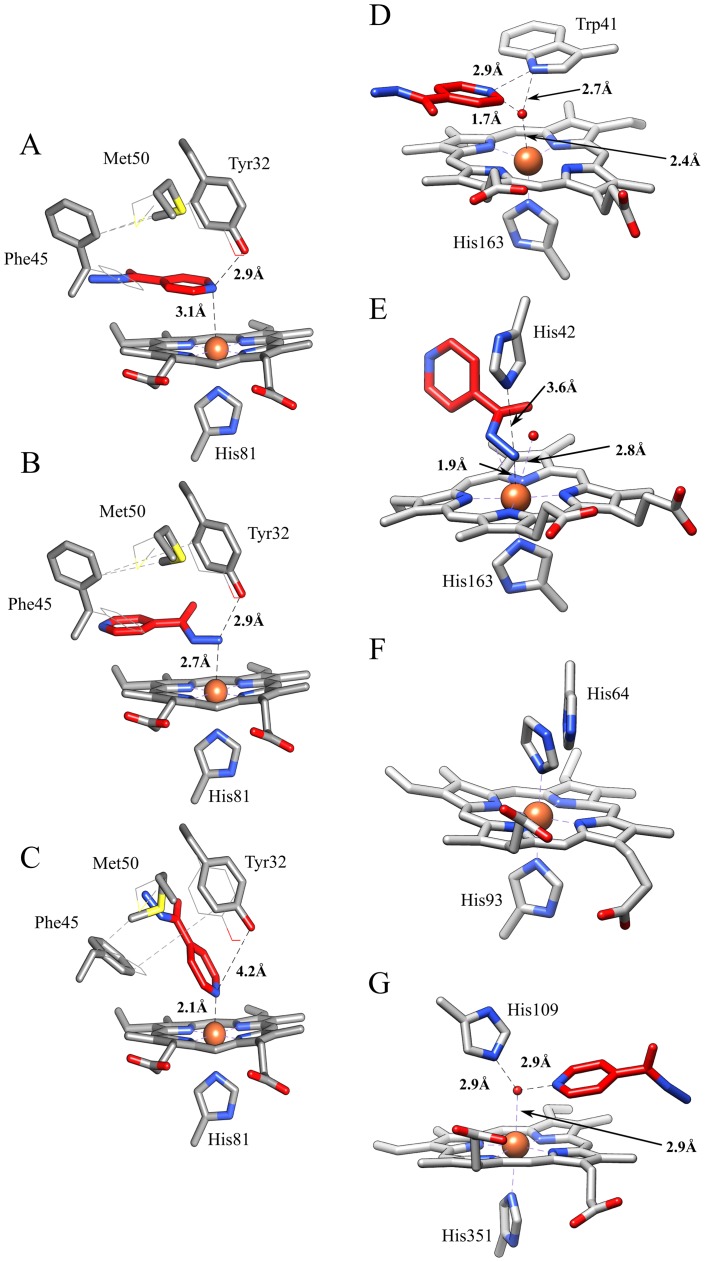
Figure 7. Binding modes of isoniazid to Mt-trHbN (panels A-C; present study) and related heme-protein systems (panels D-F).
(A) The pyridine moiety of isoniazid is parallel to the heme plane of Mt-trHbN, and the pyridine nitrogen is at a H-bonding distance from the hydroxyl group of Tyr32. (B) The hydrazone group of isoniazid interacts with the heme-Fe atom of Mt-trHbN. (C) Isoniazid interacts with the heme-Fe atom of Mt-trHbN through the pyridine nitrogen atom. (D) Isoniazid interacts with the His42Ala mutant of sAPX by the pyridine group (PDB-ID: 2VCN). (E) Isoniazid binds to the Trp41Ala mutant of sAPX by the hydrazone group (PDB-ID: 2VCS). (F) Imidazole binding to ferric sperm whale myoglobin (PDB-ID: 1MBI). (G) Isoniazid binding to bovine lactoperoxidase (PDB-ID: 3I6N). In panels A-C, isoniazid is represented in red sticks; moreover, the heme, the proximal His81 residue, and the flexible residues Tyr32, Phe45, and Met50 are shown. Furthermore, the original conformations of the flexible residues are represented as lines. In panels D-G, only the heme, the heme proximal residue (His163, His163, His93, and His351, in panels D, E, F, and G, respectively), the heme distal residue (Trp41, His42, His64, and His109 in panels D, E, F, and G, respectively), the heme-bound ligand (isoniazid or imidazole) and the closest water molecules are shown. The distance between Tyr32 and the heme-Fe atom is not reported in panels A-C as in all the cases is longer than 5.5 Å ruling out any interaction. For details, see text.