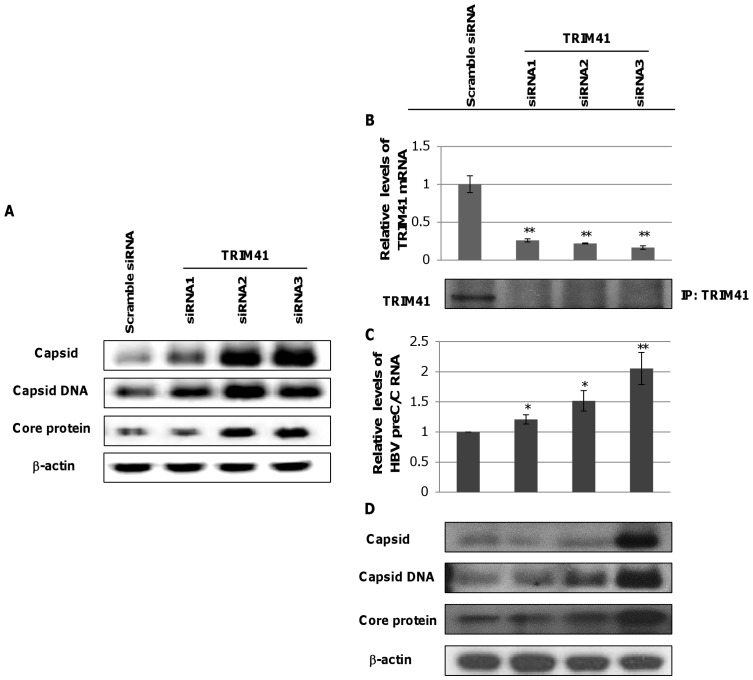
Figure 7. Endogenous TRIM41 inhibits HBV transcription in HepG2 cells.
(A) HepG2 cells in 12 well plates were transfected with 20 nM of scramble siRNA or one of three siRNA specifically targeting TRIM41. Six hours later, the cells were co-transfected with 0.4 µg of pHBV1.3 and 0.4 µg of a plasmid expressing TRIM41. The cells were re-transfected with 20 nM of siRNA 24 hours later and harvested at 48 hours post pHBV1.3 and TRIM41-expressing plasmid transfection. Core protein was tested by Western blot with β-actin as a loading control. Capsid and capsid DNA were analyzed by a particle gel assay. (B) 15 nM of TRIM41 siRNAs or scramble siRNA were transfected into HepG2.2.15. Two days post transfection, cells were harvested. The total cellular RNAs were extracted and reverse transcribed. TRIM41 siRNA knockdown efficiency was tested by quantification of TRIM41 mRNA level with a quantitative RT-PCR assay (upper panel). The level of TRIM41 protein in the transfected cultures were determined by immunoprecipitation and Western blot assays with a polyclonal antibody against human TRIM41 (lower panel). (C) HBV preC/C RNA and total viral mRNA were quantified by a quantitative RT-PCR assay and normalized with β-actin mRNA as an internal control. (D) Core protein, capsid and capsid DNA levels were tested by Western blot or Southern blot assays. The same amounts of cell lysates were loaded after BCA quantification. The level of β-actin was used as a loading control. The mean and standard deviations (n = 4) were presented. * and ** indicate P<0.05 and 0.01, respectively.