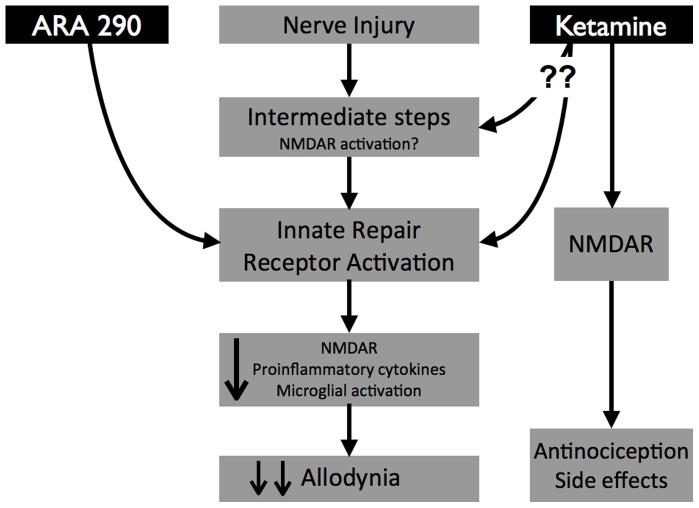
Figure 6. Neuropathic pain involves a pathway that utilizes the Innate Immune Receptor.
Nerve injury results in microglial recruitment, increased expression of NMDAR, and proinflammatory cytokine production, ultimately resulting in allodynia. Activation of the innate immune receptor (IRR), e.g., by ARA 290, antagonizes this pathway. Ketamine also requires the IRR to reduce allodynia. This may be via a direct interaction with the IRR or alternatively, via modulation of intermediate processes that are upstream of the IRR. Additionally, ketamine interacts with NMDARs that mediate antinociception and psychomotor effects. ARA 290 does not interact with the NMDAR and therefore lacks these additional effects.