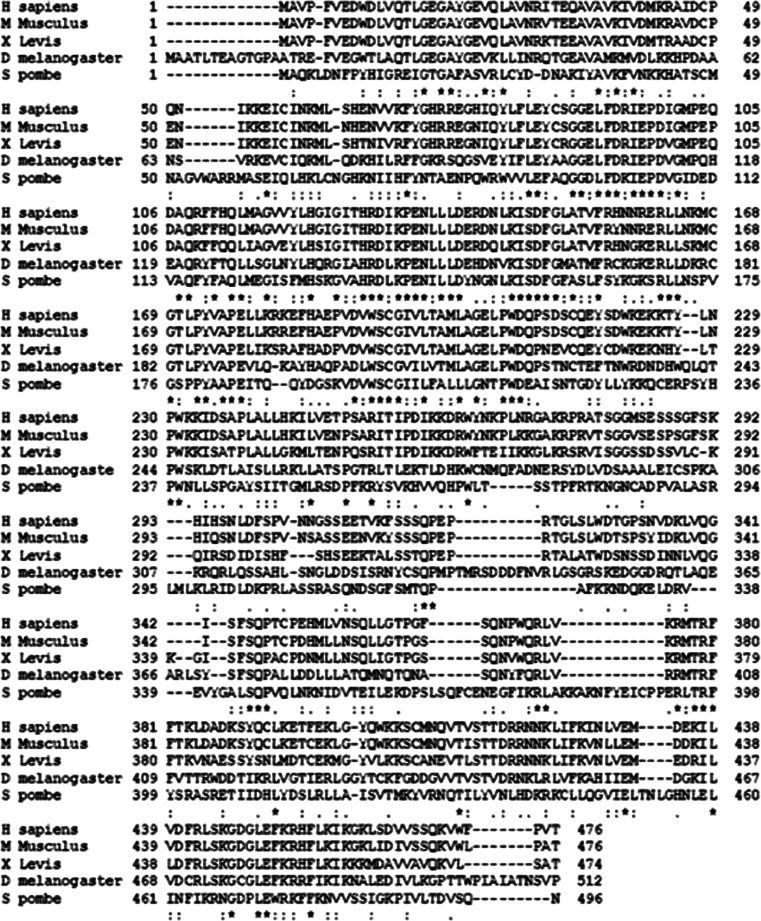
Fig. 7.
CHk1 sequence alignment between human, mice, fruit fly, Xenopus and yeast. Chk1 sequences of human, mice, Drosophila, Xenopus, and yeast were analyzed using T-coffee, a Web server for multiple sequence alignment tool. The N-terminal kinase domain and regulatory SQ/TQ domain of Chk1 are highly conserved, while the C-terminal domain is less conserved. Asterisk indicates highly conserved sequence, Colon indicates conserved substitution, Dot indicate semi conserved substitutions