Fig. 3.
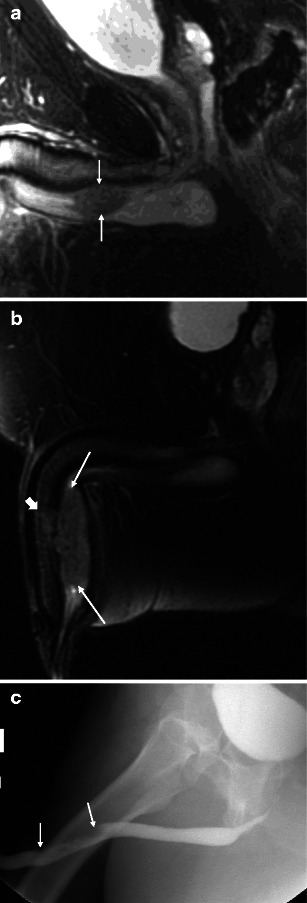
a Malignant male tumour: stage II bulbar urethral squamous cell carcinoma. The patient presented with a palpable non-tender mass. Sagittal T2-weighted image demonstrates a bulbar urethral mass invading the corpus spongiosum (arrows). b Malignant male tumour: stage III penile urethral squamous cell carcinoma. In a different patient, sagittal T2-weighted image demonstrates a large penile urethral mass involving the corpus sponsiosum (arrows) and focally invading the tunica albuginea and corpora cavernosa (block arrow). c Malignant male tumour: penile urethral squamous cell carcinoma. Retrograde urethrogram of the same patient as b demonstrates irregular narrowing of the penile urethra secondary to the mass (arrows). The full extent of the mass and the corpora cavernosa invasion is not appreciated by this modality
