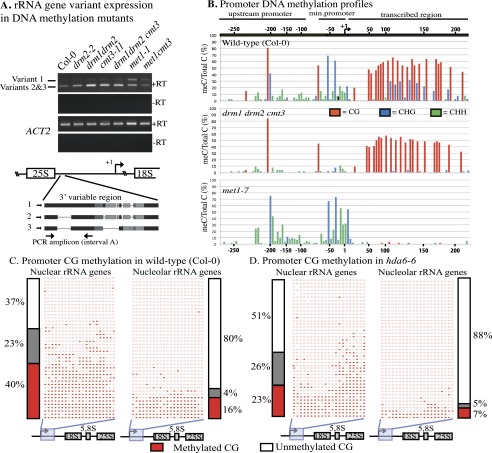
Figure 2.
MET1-dependent CG methylation is required for variant 1-type rRNA gene silencing. (A) rRNA gene variant expression in wild type (Col-0) or drm2-2, drm1 drm2, cmt3-11, drm1 drm2 cmt3, met1-1, or met1 cmt3 mutants. RT–PCR using primers that discriminate variant 1- from variant 2- and 3-type rRNA genes was conducted (see the diagram for primer locations). RT–PCR of ACTIN2 (ACT2) mRNA serves as a positive control. Reactions lacking reverse transcriptase (−RT) serve as negative controls. (B) Frequencies at which individual cytosines are methylated between −316 and +243 relative to the transcription start site (+1), determined by bisulfite sequencing. Wild-type Col-0, drm1 drm2 cmt3 triple mutants, and met1-7 mutants are compared. Approximately 40 independent promoter clones were sequenced for each genotype. Cytosine-depleted regions are compressed on the X-axis. (C,D) Cytosine methylation in the downstream promoter region of rRNA genes in purified nuclei or nucleoli from wild-type or hda6 leaves, determined by bisulfite sequencing. Positions of methylated (filled circles) or unmethylated (open circles) cytosines in CG motifs of 43 independent promoter clone sequences are shown. Methylation haplotypes are grouped according to methylation density. Histograms show frequencies of hypomethylated haplotypes (white), haplotypes with intermediate methylation (gray), or heavily methylated haplotypes (red).