Figure 9.
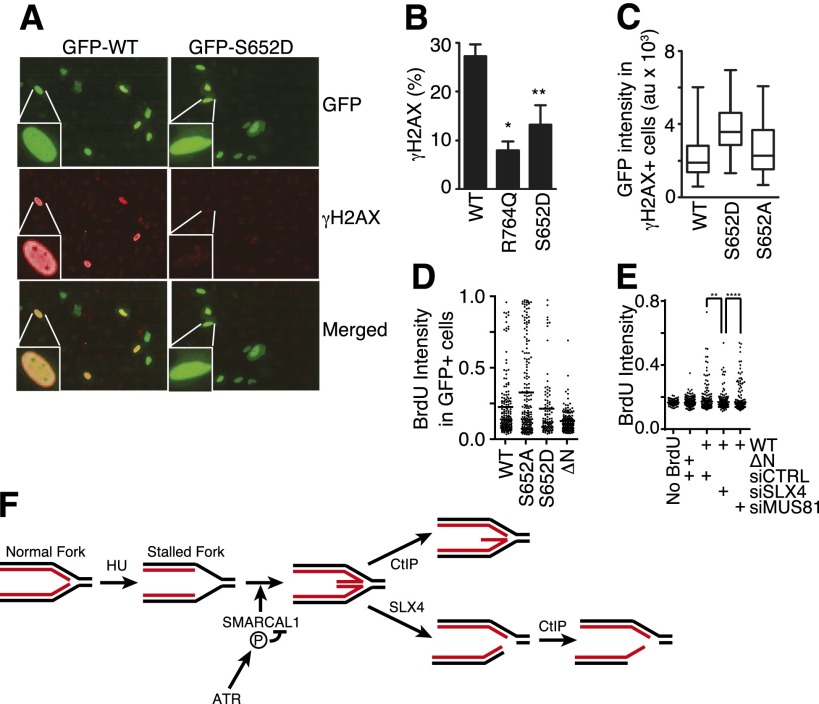
Phosphorylation of SMARCAL1 at S652 decreases its activity at DNA replication forks in cells. (A–C) GFP-SMARCAL1 wild-type and mutant proteins were overexpressed in U2OS cells. Cells were stained with DAPI to mark the nucleus and antibodies to γH2AX. Images were acquired using an Opera automated confocal microscope, and the levels of GFP-SMARCAL1 and γH2AX levels were quantitated in each nucleus using Columbus software. (A) Representative images. (B) Data represent the percentage of cells expressing between 500 and 2500 arbitrary units of GFP-SMARCAL1 that contain a mean γH2AX intensity of >1000 arbitrary units. Error bars represent SEM from three independent experiments. (*) P = 0.0007; (**) P = 0.023. (C) The expression level of GFP-SMARCAL1 (as measured by GFP intensity) in each cell that had a γH2AX intensity of >1000 arbitrary units is plotted in box and whisker format; significantly higher GFP-SMARCAL1 S652D protein levels were needed to induce γH2AX than either wild-type or S652A protein (P < 0.0001). (D) GFP-SMARCAL1 proteins with the indicated mutations were expressed in U2OS cells. BrdU was added to the culture medium 16 h prior to fixation and staining in nondenaturing conditions to measure the total level of ssDNA. The mean intensity (arbitrary units) of BrdU staining per GFP-SMARCAL1-expressing cell is graphed. The line indicates the mean value in each population (Mann-Whitney test, S652A vs. S652D; P = 0.013). (E) GFP-SMARCAL1 proteins were expressed in U2OS. These cells were then transfected with control, MUS81, or SLX4 siRNA. BrdU was added to the culture medium 16 h prior to fixation and staining in nondenaturing conditions to measure the total level of ssDNA. The mean intensity (arbitrary units) of BrdU staining per cell is graphed. The line indicates the mean value in each population (Mann-Whitney test, siCTRL vs. siSLX4; P = 0.0012; siSLX4 vs. siMUS81; P < 0.0001). (F) Model for nascent-strand ssDNA generation at stalled forks. Black and red lines represent template and nascent strands, respectively. HU causes uncoupling of the replicative helicase and polymerases, resulting in template-strand ssDNA at the replication fork. ATR prevents aberrant fork remodeling by the SMARCAL1 enzyme. In the absence of ATR-dependent SMARCAL1 S652 phosphorylation, a Holliday junction-like structure may persist at the fork and is cleaved by SLX4-dependent nucleases, generating a DSB. CtIP-dependent nucleases then resect the break, yielding nascent-strand ssDNA. CtIP may also process a reversed fork structure prior to SLX4 cleavage, which could contribute to the nascent-strand ssDNA formation.