Figure 3.
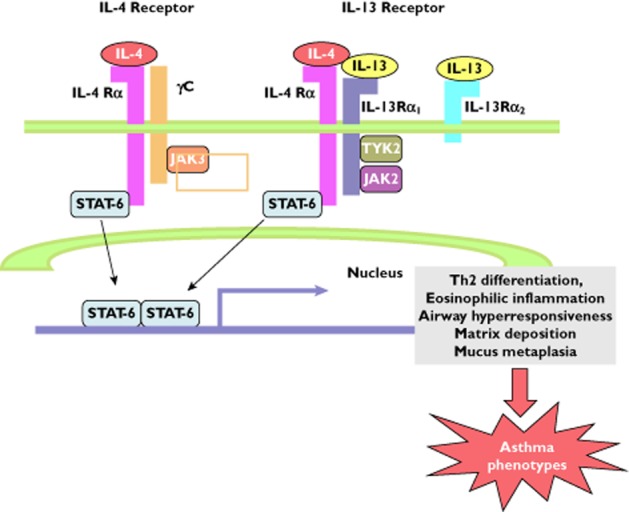
Schematic diagram of the interleukin (IL)-4/IL-13 signal transducer and activator of transcription factor (STAT)-6 signalling pathways linked to T-helper 2 (Th2)-type inflammation. Interleukin-4 and IL-13 are recognized by IL-4Rα, a component of the IL-4 type I (IL-4Rα and γC) and type II receptors (IL-4Rα and IL-13Rα1). Interleukin-4 signals through both type I and type II receptor pathways, whereas IL-13 signals only through the type II IL-4R. Interleukin-13 also binds to the IL-13Rα2 chain with greater affinity, lacking a transmembrane-signalling domain, but functions to interfere with janus kinase (JAK) 2 activation in the IL-4Rα/ IL-13Rα1 complex as well as functioning as a decoy receptor to down-regulate IL-13 signalling. γC activates JAK3, while IL-13Rα1 activates tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) and JAK2. Activated JAKs phosphorylate STAT-6 which, upon dimerization, translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to the promoters of the IL-4- and IL-13-responsive genes associated with Th2 cell differentiation, airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness, fibrosis and epithelial mucous metaplasia (Adapted from reference 105; reproduced with permission of Trends in Immunology)
