Fig. 1.
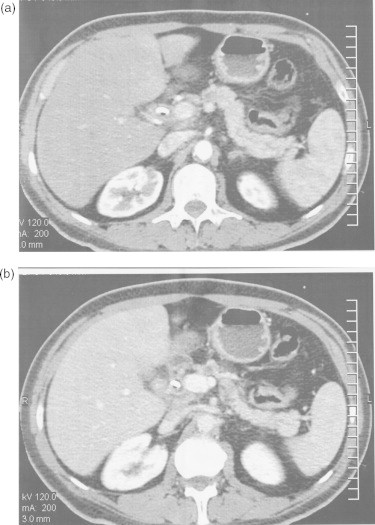
Transverse contrast-enhanced (a) arterial and (b) portal phase CT images demonstrated interruption of the pancreatic duct in the neck portion, as well as upstream pancreatic duct dilatation. Images did not provide visualization of mass.

Transverse contrast-enhanced (a) arterial and (b) portal phase CT images demonstrated interruption of the pancreatic duct in the neck portion, as well as upstream pancreatic duct dilatation. Images did not provide visualization of mass.