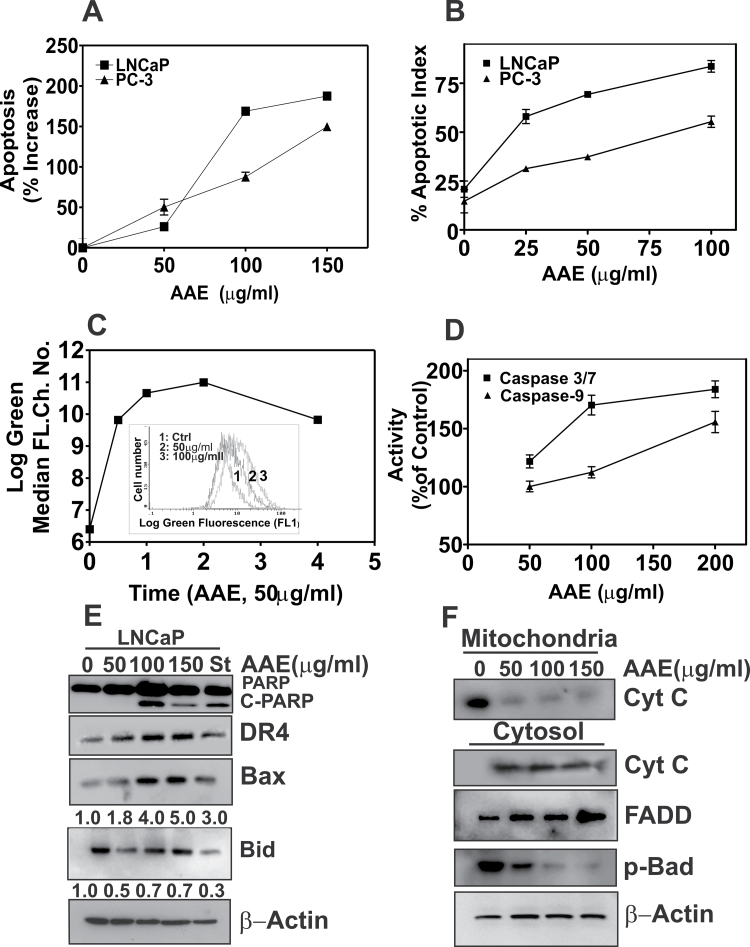
Fig. 2.
The cytotoxicity of AAE is due to apoptosis. (A) Apoptosis in LNCaP and PC-3 cells treated with AAE for 48 h. Levels of H1 histone in cell lysates prepared from AAE-treated samples, indicative of apoptosis, were determined using a kit followed by the procedure described in the kit manual (Cell death ELISA Plus; Roche Applied Sciences, Indianapolis, IN). Results are expressed as % increase from untreated cultures (three replicates). Also see Supplementary Table S1, available at Carcinogenesis Online; (B) Apoptosis index determined by TUNEL assay of cells treated with AAE (48 h). LNCaP and PC-3 cell cultures were treated with AAE for 48 h and assayed for DNA fragmentation due to apoptosis using a TUNEL assay kit that fluorescently labels the cells undergoing apoptosis. Confocal imaging was used to enumerate fraction of cell population in a given field (total of 4 fields/treatment) that are fluorescent. Data are presented for a single experiment; similar data were obtained in two replicate experiments. Representative micrographs of AAE-treated and TUNEL-positive cells are presented in Supplementary Figure S1A, available at Carcinogenesis Online. (C) Decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential in AAE-treated LNCaP cells. Cell suspensions prepared from cultures treated with AAE over 48h were incubated with potential-sensitive mitochondrial dye JC-1 for 30min followed by determination of green fluorescence intensity by flow cytometry, as described (16). Time course of relative accumulation of monomeric JC-1 dye with and without AAE treatment is shown. Time was represented as hours in the graph. Inset: Levels of ROS in LNCaP cells after exposure to AAE. Increased accumulation of carboxy-6-carboxy-2′7′-dicholorohydroxy fluorescein is shown as right shift in median log fluorescence channel. (D) Caspases activation by AAE in LNCaP cells (24h). Caspases 3/7 and 9 activities were measured using a kit (Promega). Results are presented as mean ± SD, for three independent replicate experiments. (E) Levels of C-PARP, DR4, Bax, Bid and cleaved-BID (C-Bid) in LNCaP cells treated with AAE for 24h. Cell lysates prepared form AAE-treated cultures for 24 h were fractionated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting as described previously (16). Blots were re-probed for β-actin to normalize total protein loading. Doses of AAE are shown at top of the panel (0–150 µg/ml) and staurosporin (St) used as positive control for apoptosis induction. (F) AAE causes intrinsic apoptosis by cytochrome-C release from mitochondria. The mitochondria and cytosol fractions of AAE-treated LNCaP cells for 24 h were isolated and analyzed by immunoblotting. Note the increased levels of cytoplasmic-cytochrome-C in AAE-treated cell cultures. Increased levels of FADD and decreased level of phospho-Bad were also seen in cells treated with AAE for 24 h.