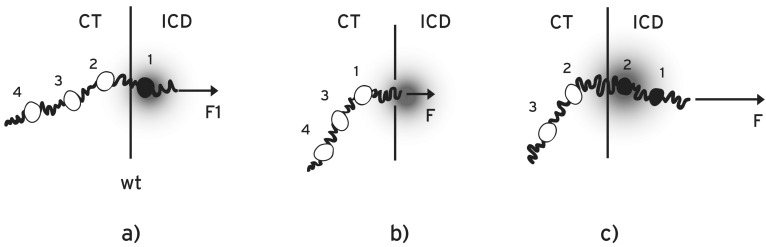
Fig. (3).
Posterior Hox gene manipulations. a) In the wt Hox cluster the posterior end (5’) is fixed but the anterior end (3’) is loose and a small force F1 pulls Hox1 (black disc) from CT to ICD in the region of the transcription factoty. b) When Hox2 is deleted N diminishes and the force F1 decreases to F. F does not suffice to extrude Hox1 from the CT to the ICD. According to Eq. (1) (F = P*N) for the extrusion of Hox1, F must increase to F1(posteriorization). c) When Hox2 is duplicated N increases. Hence a stronger force F pulls both Hox1 and Hox2 inside the ICD. Hox1 moves away from the TF domain.