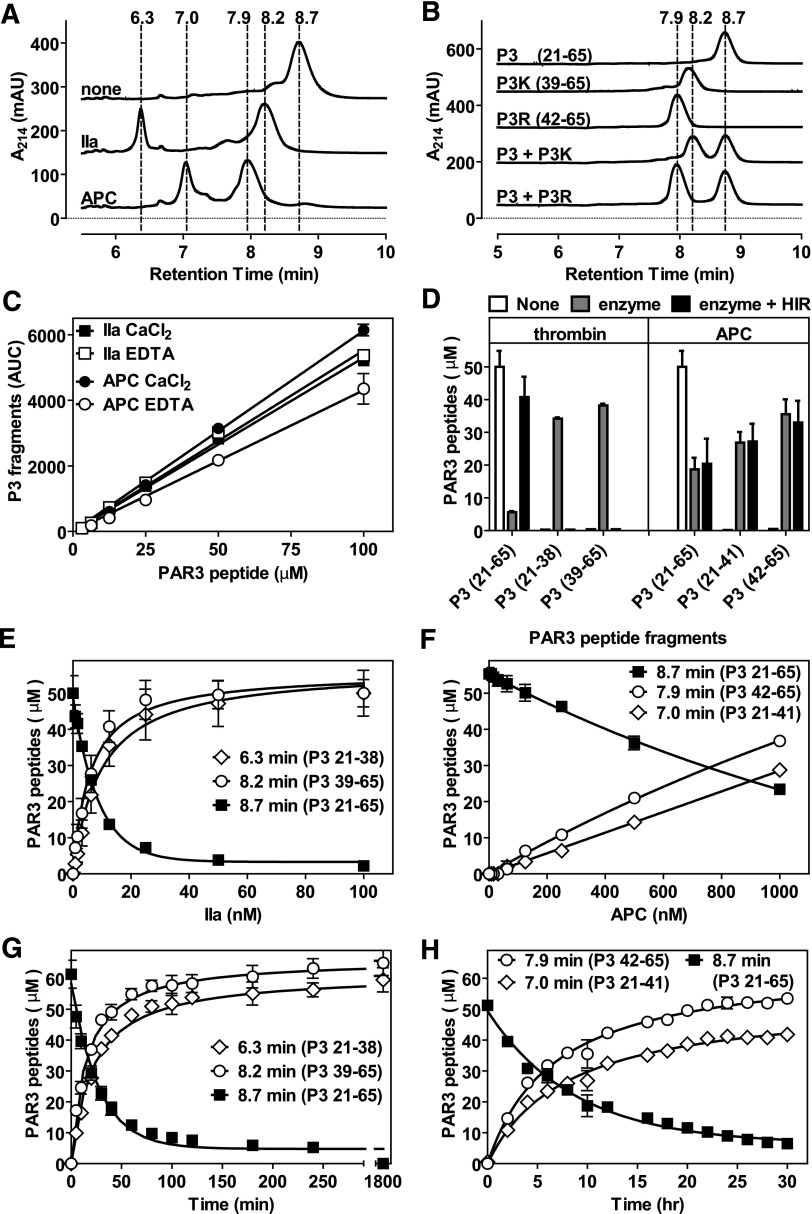
Figure 2.
Proteolysis of a synthetic PAR3 peptide by APC and thrombin. (A) Chromatogram of P3 fragments generated after 48 hours in the absence (none) or presence of APC (500 nM) or thrombin (IIa) (10 nM). (B) Chromatogram of the P3 parental peptide and synthetic peptides representing the predicted C-terminal cleavage fragments generated by APC (P3R) and thrombin (P3K). (C) Generation of P3 N-terminal cleavage fragments by APC (500 nM, 9 hours; fragment [21-41], Rt 7.0 minutes) and thrombin (10 nM, 2 hours; fragment [21-38], Rt 6.3 minutes) in the absence of divalent metal ions (2 mM EDTA) or in the presence of 2 mM CaCl2 and 0.6 mM MgCl2. (D) Generation of P3 N- and C-terminal cleavage fragments by APC (500 nM, 10 hours) and thrombin (10 nM, 2 hours) in the absence and presence of 100 U/mL hirudin (HIR). (E) Concentration-dependent cleavage of the P3 peptide by thrombin (1 hour). (F) Concentration-dependent cleavage of the P3 peptide by APC (10 hours). (G) Time-dependent cleavage of the P3 peptide by thrombin (10 nM). (H) Time-dependent cleavage of the P3 peptide by APC (500 nM). (A-B) Representative chromatograms. (C-G) Data points represent the mean ± SD (n ≥ 3).