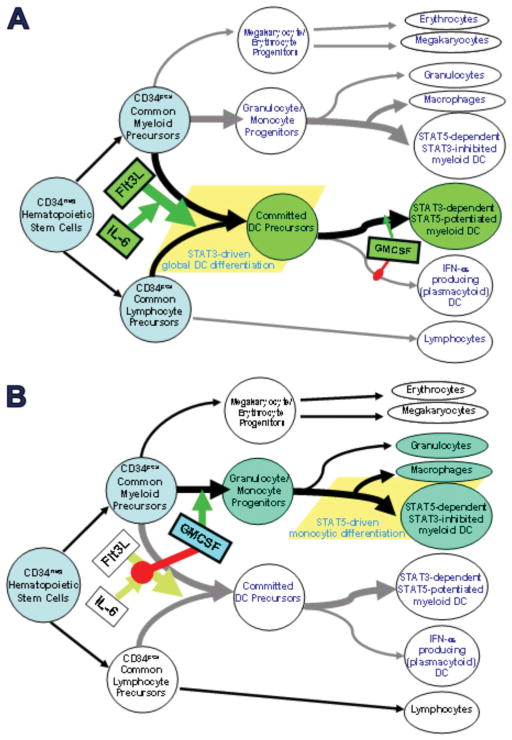
Figure 12.
Physiologic regulation of normal hematopoiesis by STAT3 vs STAT5 activating agents. Flt3L stimulates pan-differentiation of CD34pos common myeloid and common lymphocyte precursors into CD11cpos committed DC precursors via a STAT3-dependent process. This is markedly potentiated by IL-6 and G-CSF, but is dominantly suppressed by early exposure to GMCSF, due to inhibition of STAT3 activation and concomitant STAT5 activation. Such early GMCSF exposure instead favors differentiation of CD34pos common myeloid precursors into granulocyte/monocyte progenitors (rather than committed DC precursors). The granulocyte/monocyte progenitors achieve subsequent multilineage differentiation, including STAT5-dependent differentiation into conventional DCs and macrophages, and STAT5-independent differentiation into neutrophils. Phenotypically conventional DCs generated by STAT3- vs STAT5-dependent pathways differ in many critical characteristics. It should be emphasized that although early exposure to GMCSF blocks STAT3-dependent DC differentation, later exposure of committed DC precursors to GMCSF may instead promote maturation and DC1-polarization, again by stimulating STAT5 and inhibiting STAT3.