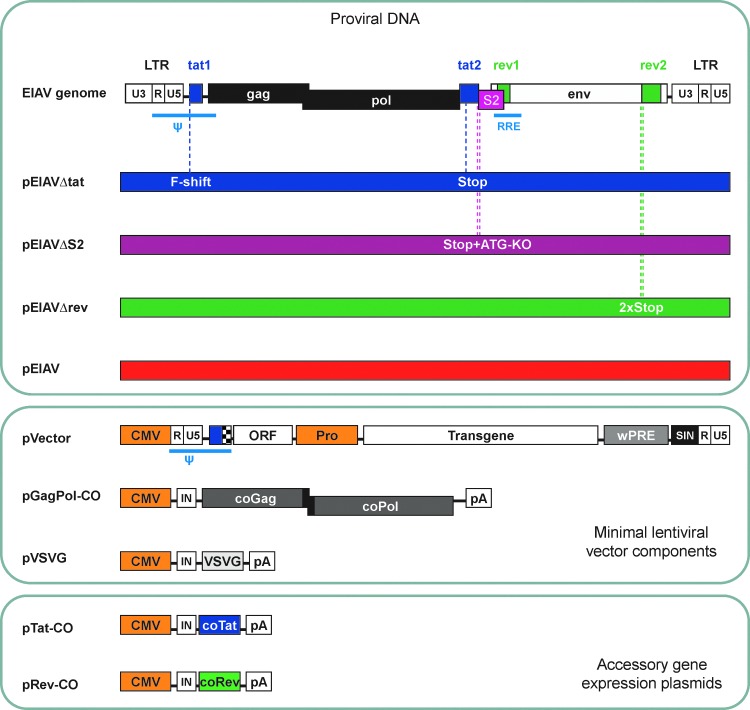
FIG. 3.
DNA constructs generated in this study and EIAV vector system components. The EIAV genome structure is simple, encoding only three accessory genes: tat, rev, and S2. To reduce the chance of mutation reversion occurring during infection studies, mutant EIAV proviral DNAs each contained two mutations to abrogate expression of the respective accessory protein. Color coding of these genomes is maintained in subsequent figures. F-shift, frameshift mutation; Stop, translation stop codon; ATG-KO, translation start knockout; ψ, packaging signal; RRE, Rev-responsive element; ORF, open reading frame; Pro, promoter; IN, synthetic intron; wPRE, woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element; SIN, self-inactivating LTR; CO, codon-optimized; LTR, long terminal repeat.