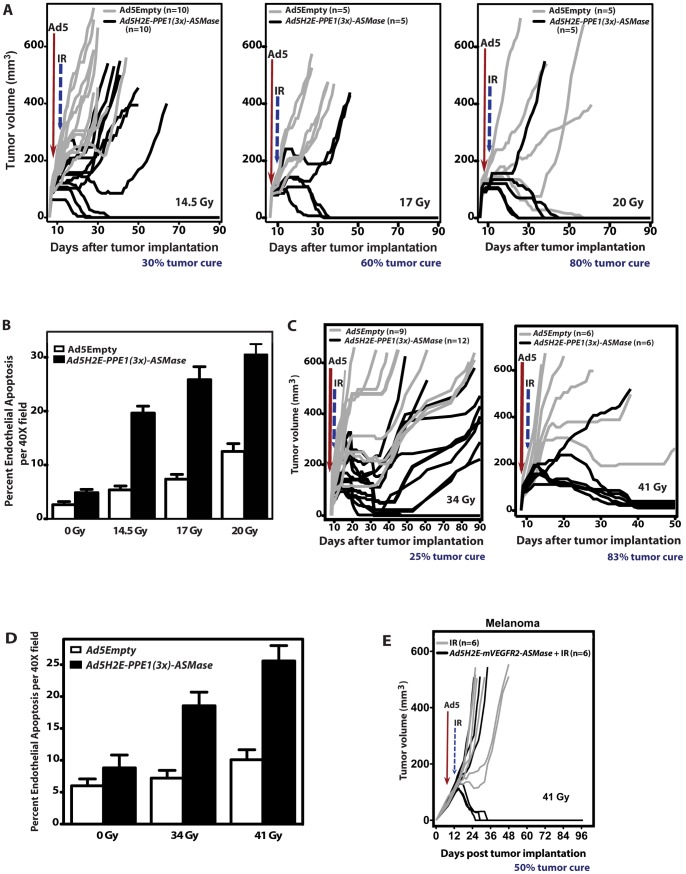
Figure 6. ASMase overexpression in tumor endothelium radiosensitizes MCA/129 fibrosarcomas and B16 melanomas.
1×1010 PFU of Ad5Empty or Ad5H2E-PPE1(3x)-ASMase was administered intravenously to MCA/129 fibrosarcoma- (A,B) and B16 melanoma (C,D)-bearing sv129/BL6JAX mice, as in Figure 5. Five (A,B) or four (C,D) days post virus administration tumors were locally irradiated with 14.5, 17 Gy and 20 Gy (A,B), or 34 and 41 Gy (C,D). (A,C) Response of MCA/129 fibrosarcoma (A) and B16-F1 melanoma (C) to Ad5Empty (gray lines) or Ad5H2E-PPE1(3x)-ASMase (black lines) followed by IR. N = animals/group. Tumors were measured daily up to 40 days and twice weekly thereafter. Tumor cure was confirmed by local biopsy. (B,D) Quantitation of the impact of Ad5H2E-PPE1(3x)-ASMase on radiation-induced endothelial cell apoptosis within MCA/129 fibrosarcomas (B) and B16-F1 melanomas (D) implanted into sv129/BL6JAX asmase+/+ mice. Data (mean ± SEM) represent TUNEL-positive endothelial cells quantified from 20 (400× magnification) fields/tumor using 2 tumors/group. (E) ASMase overexpression in tumor endothelium using the murine VEGFR2 promoter radiosensitizes B16 melanoma. 2×1010 PFU of Ad5H2E-mVEGFR2-ASMase was administered intravenously to B16 melanoma-bearing sv129/BL6JAX mice. Five days thereafter tumors were locally irradiated with 41 Gy. B16 melanoma response to Ad5H2E-mVEGFR2-ASMase and irradiation (black lines) or radiation alone (gray lines) are presented as tumor volumes.