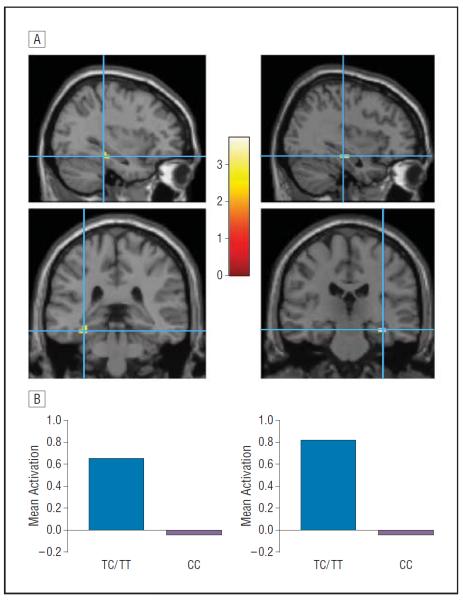
Figure 3.
FKBP5 polymorphism is associated with differential hippocampal activation during attention to threat. A, Statistical parametric maps of left and right hippocampus activation during the processing of threat probe-incongruent vs threat probe-congruent faces in TC/TT>CC genotype. Activations are shown overlaid onto a canonical T1 magnetic resonance image. The colored bar represents t scores for activations. Maximally activated voxels from the left parahippocampal gyrus (x, y, z: −36, −35, −8) and right hippocampus (x, y, z: 36, −24, −12), P<.05 (small-volume correction, family-wise error). Data are reported using the coordinate system of Talairach and Tournoux. B, Genotype differences in averaged blood oxygen level–dependent signal (contrast time series extracted from 6-mm spherical regions of interest) to this contrast condition.