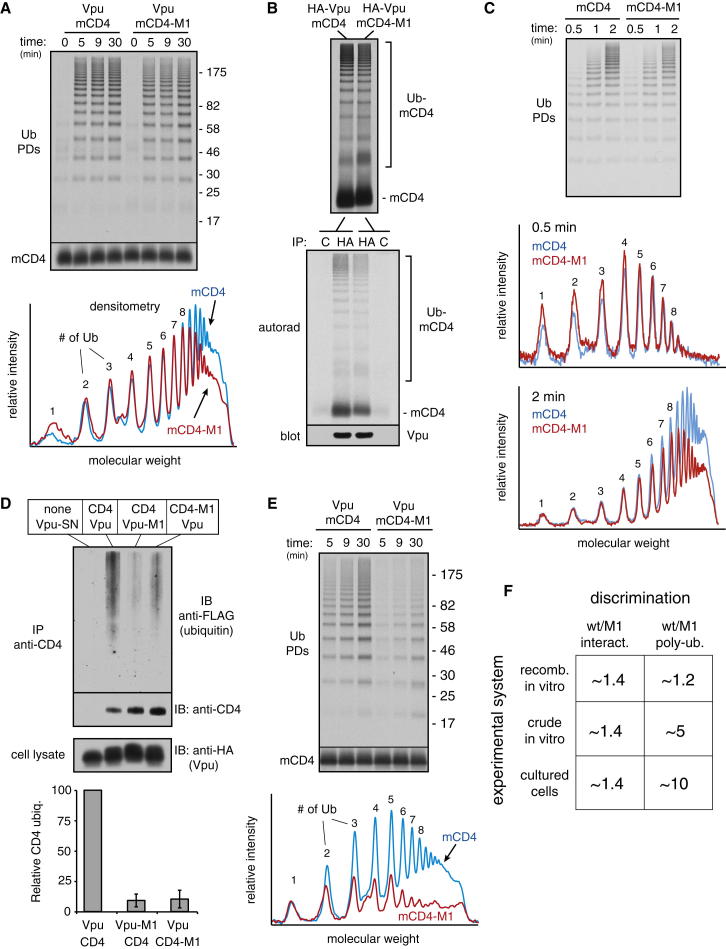
Figure 4.
Substrate Discrimination in Cells, In Vitro, and in Purified Systems
(A) Analysis of discrimination in a radiolabeled recombinant ubiquitination system. Radiolabeled mCD4 (or mCD4-M1) isolated from in vitro translation reactions (see Figure S4A) was coreconstituted with recombinant Vpu into liposomes. The purified proteoliposomes were subjected to ubiquitination with recombinant SCFβTrCP, purified E1 and E2 enzymes, His6-tagged ubiquitin, and ATP. The reaction at different time points was stopped and analyzed for ubiquitinated mCD4 via pull-downs of the tagged ubiquitin (Ub PDs). Total mCD4 in the reaction is shown in the bottom panel. The graph below the autoradiograph depicts the densitometry profiles of the 5 min samples, with the individual ubiquitinated species indicated.
(B) Ubiquitination reactions as in (A) were either analyzed directly (top) or after solubilization and native IP using anti-HA or control antibodies (bottom). The HA-tagged Vpu recovered in the IP was analyzed by blotting, and the mCD4 was analyzed by autoradiography.
(C) Analysis of ubiquitination reactions as in (A) at short time points.
(D) CD4 ubiquitination in cells. The indicated combinations of Vpu and CD4 were cotransfected with FLAG-ubiquitin, treated with proteasome inhibitor (40 μM MG132) for 5 hr, subjected to IP with anti-CD4, and analyzed by immunoblotting for FLAG-ubiquitin and CD4. Vpu levels in the lysate are also shown. The graph shows quantification (mean ± SD; n = 3) of relative CD4 ubiquitination normalized to total CD4.
(E) Ubiquitination reactions of in vitro translated mCD4 or mCD4-M1 in Vpu-containing HEK293 microsomes. Quantification of the 30 min time point is shown below the autoradiograph.
(F) Summary of the results of interaction and ubiquitination analysis from cell culture, crude in vitro, and recombinant in vitro systems. The approximate ratios of wild-type (wt) to M1 mutant recovered by co-IP (interaction) and observed to be polyubiquitinated are indicated. The recombinant in vitro system shows poor discrimination.
See also Figures S4 and S5 and Tables S1 and S2.