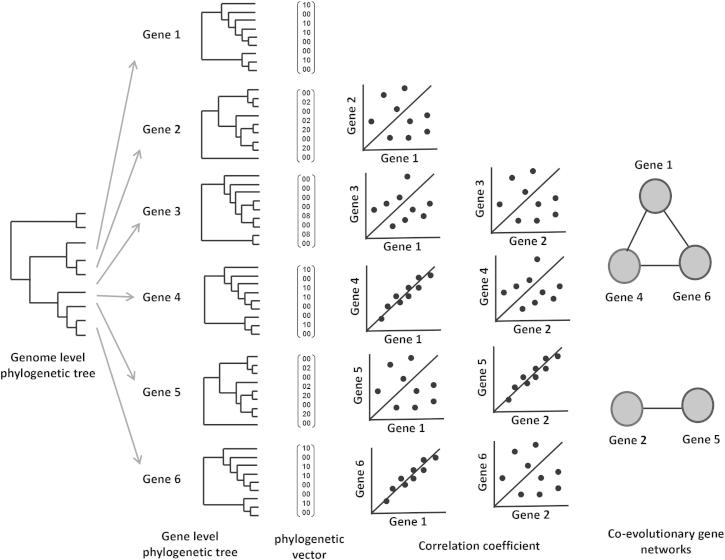
Figure 2.
Illustration of the Mirror Tree Approach
In this illustration, hypothetical genes 1, 4, and 6 evolved together, as they show identical phylogenetic history, whereas genes 2 and 5 also show an identical evolutionary history, though these two groups of genes evolved at a different evolutionary rate. These evolutionary patterns of individual genes were converted into phylogenetic vectors. Phylogenetic vectors of coevolving genes such as genes 1, 4, and 6 are more highly correlated than those that evolved at different rates such as genes 2 and 6. Networks of genes that coevolved were generated from significantly correlated genes. Phylogenetic vectors were derived by taking into account population structure.